The goal of this blog is to clear common queries regarding the FRCR exam, its pattern, and the strategy for preparation. I have not appeared for the exam and I am as ignorant as you guys are. This blog has been originally written by Dr. Inthulan Thiraviaraj and has undergone regular revisions since then. If you have any suggestions or edits, please reach out to us using the contact form or let us know in the comments section below. Do note that this blog answers questions pertaining to the Clinical Radiology Exam only. The Clinical Oncology exam is not covered in this blog.
Table of contents
Introduction:
Most of you first heard about the FRCR exam during residency and would know friends or seniors giving this exam. You might have given one or two steps yourself but still have questions about the time taken to complete, expenses involved, advantages of the degree, study materials required, courses available, and how to approach the exam. I obtained my FRCR in May 2018 but my journey began in March 2015, a few months after my residency at KEM! My understanding of the exam has helped me guide many of my friends and colleagues and when Amar approached me to write this chapter for his website, I found the perfect opportunity to share my insight with all of you. This is primarily for radiologists trained in India and answers the poll we posted a few days ago. A number of changes have also occurred in the past 2 years relating to the conduct of exams and the readers are directed to refer to the official website for the latest updates. I have tried to give you an overview of the exam, introduce you to the components, help you plan your pathway, and provide relevant information that is otherwise unavailable on official sites. Relevant links to books and for further reading are provided in the subsections.
Overview of the FRCR exam:
What is the FRCR exam / What is the full form of FRCR / What does FRCR stand for?
FRCR stands for Fellow of Royal College of Radiology. The FRCR Exam is a three-step examination conducted by the Royal College of Radiologists (UK) after which the candidate is inducted as a Fellow of the RCR.
How many steps to complete the exam and obtain the degree? There are three steps involved.
- First FRCR Examination (FRCR Part 1) – Two modules:
- Anatomy
- Final FRCR Part A Examination (FRCR2A): Two MCQ based written papers.
- Final FRCR Part B Examination (FRCR 2B):
- Reporting.
- Rapid Reporting.
- Oral examination.
When and where are the FRCR exams conducted?
Updated FRCR exam dates can be found on the RCR website. All three components of the exam are held in the U.K., Singapore, and Hong Kong with the schedule as follows:
| United Kingdom | Singapore | Hong Kong | |
| FRCR Part 1 | Spring (March), summer (June) and autumn (September) | ||
| FRCR2A | Summer (June) and winter (December) | ||
| FRCR 2B | Summer (Apr) & Autumn (Oct) | Summer | Autumn |
Latest information regarding dates, venues and fees can be accessed here:
Due to COVID, the rules for these exams are constantly evolving. Please check the RCR Updates website for the latest guidelines.
What are the eligibility criteria for the FRCR radiology exam?
| FRCR Part 1 | Anyone who is undergoing radiology training or has completed training can attempt FRCR Part I. There is no minimum training requirement. |
| FRCR Part 2A | After passing both modules of FRCR part 1 and with 24 months of radiology training, you can apply for FRCR 2A. Your training must be acknowledged and certified by your head of department stating that he/she has read the FRCR curriculum and that you have received adequate training in all those areas specified. Hence a letter from your HOD with relevant information, declaration, sign, signature, and date is required for your 2A application. |
| FRCR Part 2B | Once you have passed 2A, and have completed 34 months of training (similar declaration required), you can apply for 2B. |
What is the approximate time taken to complete all three steps?
If you appear for all exams consecutively, with minimum breaks, pass all exams on the first attempt, and have the best chances in ballot selection it will take 1.5 to 2 years to complete.
What is the best time in my career to undertake the exams?
- Part I is best attempted during residency.
- Best time to appear for part 2 is after your post-graduation exams. However, it is possible to attempt the exam in your 5th semester, before your M.D. exam.
Is PLAB required to sit for the FRCR exam?
No. With PLAB you can obtain a GMC registration and theoretically apply for a training post or job in the U.K.
Can I write the exam after MBBS? No. Ongoing or past radiology training is mandatory to apply for these exams.
Can I write the exam after DMRD / What is the eligibility for the FRCR exam?
You can attempt Part 1 and 2A. However, you require 34 months of supervised training, in a teaching college to apply for 2B. Hence with 24 months of DMRD alone, you will not qualify for 2B.
Can I write the exam after DNB Radiodiagnosis?
Yes.
Can I write the exam after MD Radiodiagnosis?
Most definitely.
Is there any age limit for the FRCR exam?
There is no specific documentation but in general, there is no age limit for specialty training in the UK, as per the Equality Act of 2010.
How will FRCR help me in my career in India/ What is the value of FRCR in India /What is the importance of FRCR for Indian radiologists?
- An additional degree always gives extra credit.
- More so, due to the high standards of the exam and the preparation required, your knowledge and reporting skills will definitely improve. The emphasis of the FRCR exam is to ensure that you are a SAFE radiologist. This will reflect in your practice.
- FRCR has less relevance in government service or stand-alone private practice, especially if you are a sonologist.
- Apart from personal and professional growth, FRCR will add credentials when you apply for corporate hospitals and tertiary care centers.
Will FRCR help me to practice teleradiology for foreign countries?
Yes. There are approved teleradiology services for which holding an FRCR will grant you a license to report for out-of-hours U.K. reporting. This will reflect on your earnings. That said, this should not be the only reason to apply for FRCR as the cost and effort of the exam far outweighs any potential benefit.
How will FRCR benefit me in applying for jobs in the UK?
- Once you hold an FRCR degree, you can apply for GMC registration with a license to practice. You will have to clear the IELTS exam and obtain a Good standing certificate from the Medical Council of India. You can simultaneously apply for jobs either directly or through agencies.
- At present, there are plenty of job (and fellowship) opportunities in the U.K. and is unlikely to saturate in the next 5 years.
- Interest to work, train or migrate to the U.K. is the single, most appropriate reason to undergo FRCR.
How will FRCR benefit me in countries outside the U.K.?
- FRCR is a well-recognized degree and will add weight to your application for jobs or fellowships elsewhere, especially in the Middle East and Singapore.
- After completion of FRCR, you can further your career in the U.K. and eventually apply for C.E.S.R. (Certificate of Eligibility for Speciality Training) which is the IMG equivalent of CCT (Certificate of Completion of Training). CESR will help you attain the full qualification to practice in the U.K. and will recognize you as a consultant elsewhere. I am hesitant to add anything further as I have not completed CESR myself and I do not fully comprehend the process. It is a topic for another time!
What is the probability of clearing FRCR after training in India?
There is a high probability that you will clear the exams if you are well motivated and determined. There is no point in completing one or 2 steps and giving up. The passing rate varies for each exam. It is a competency exam and not a competitive exam. How others perform is irrelevant. The physics module and FRCR2B are the most difficult to clear.
What is the passing rate for each FRCR Exam step?
| Exam | Sitting | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Average Passing Rate | Average |
|
FRCR Part 1 Anatomy
|
Spring | 85.2 | 86.7 | 87.1 | 88 | 84.8 | 86.36 |
74
|
| Summer | 78.5 | 80.9 | 59.5 | 83.5 | Cancelled | 75.6 | ||
| Autumn | 74.1 | 67.2 | 65.2 | 68.3 | 74.1 | 69.78 | ||
| Winter | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 66 | 66 | ||
|
FRCR Part 1 Physics
|
Spring | 57.2 | 66.8 | 54.3 | 55.9 | 76.2 | 62.08 |
47
|
| Summer | 51.7 | 44.4 | 57.4 | 48.5 | cancelled | 50.5 | ||
| Autumn | 45.7 | 30.8 | 42.9 | 50.4 | 80 | 49.96 | ||
| Winter | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 27.3 | 27.3 | ||
|
FRCR Part 2A
|
Summer | n/a | n/a | 51.2 | 58.8 | cancelled | 55 |
58
|
| Autumn | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 61.7 | 61.7 | ||
| Winter | n/a | 52.3 | 59.9 | 54.3 | 63.7 | 57.55 | ||
| Spring | 46.2 | 48.4 | 67.3 | 53.9 | cancelled | 53.95 |
62
|
|
| FRCR Part 2B | Autumn | 72.5 | 60.3 | 55.7 | 73.9 | 84 | 69.28 |
From this data from the RCR website for 2016-2020, the average passing rates for FRCR Exam for the past five years are as follows:
- FRCR Part 1
- Anatomy: 74%
- Physics: 47%
- FRCR Part 2: 58%
- FRCR Part 3: 62%
What is the approximate cost for each exam in total?
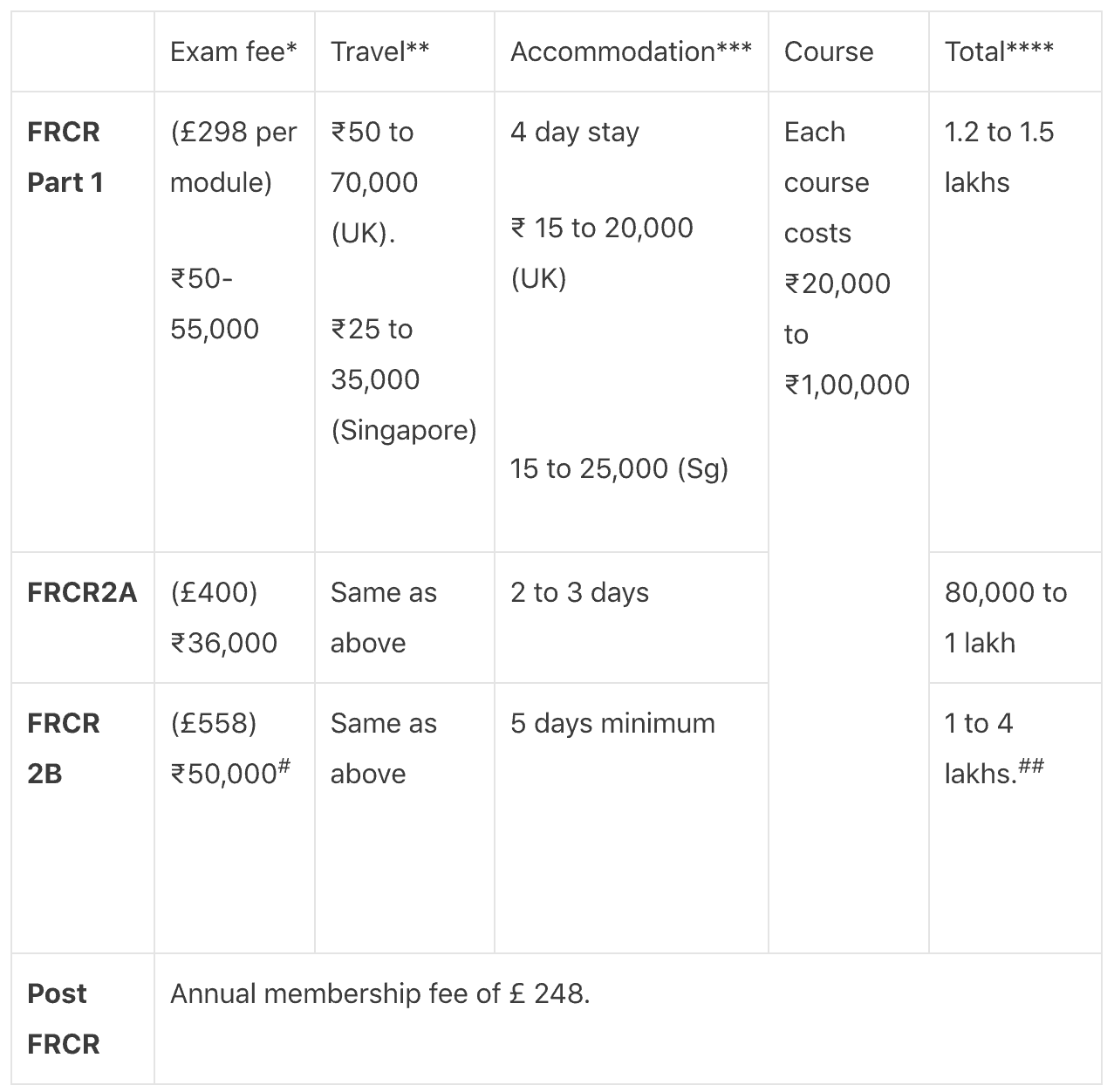
* Charges as of 2018. Consider at least 10% inflation for each year since then.
** Flight and local transport. Prices vary according to the time of booking and how early you book. Singapore visa is cheaper (~ 2500 INR) and takes 48 hours for processing. Documents required are fewer and more straightforward. UK visa (~10,000) takes longer and more is strict.
*** Stay is cheaper with shared accommodation. Recommended using tubes with a travel card for local commuting in Sg and U.K. You can always stay at an Airbnb to cut down on the budget.
Sign up using this link and get up to INR 3000 off (or the equivalent amount your respective currency) on your first booking!
**** Not inclusive of tourism and shopping!
# 2B in Singapore has to be taken along with MMed which costs 3,790SGD (₹1,90,000). You cannot apply for the FRCR2B exam alone in Singapore.
## For my FRCR exam in April 2018, I stayed in the U.K. for 1 month, attended 2 courses, shared accommodation with two of my friends, and spent a week sightseeing. It cost us 5 lakhs each, all-inclusive.
- Hong-Kong visa has pre-arrival registration for Indian citizens. The process is online and is free of cost. Read more: Pre-arrival Registration (PAR) Hong Kong.
- Affordable localities in Singapore for the FRCR exam: Little India and Geylang.
Check out our conferences page for useful tips for planning your travel and accommodation!
How do I prepare myself to apply for the FRCR exam?
- Create an account on the RCR applications website. Use your primary email address, as the college will send all communications to this email address.
- Keep all relevant documents ready.
- Fee payments need to be made using a credit or debit card, so make sure you have enough balance, and your card allows international transactions. If you are interested in cheap international payments and transfers, you can check out Wise. Sign up using this link to make your first free transfer. You can also use the Wise Card when you visit the UK/Europe/US/Most international destinations for the best conversion rates and the least charges.
- Currently, applications are being processed on a first-come, first-serve basis.
- Applications will open at 9:00 AM and close at 17:00 (UK time) on the closing date for each priority. Click here to check timings as per your time zone
- If you have special requirements, check out this document from the RCR. You will have to upload the relevant documents at the time of the application.
What is Priority 1 and 2 for the FRCR Exam?
Recently the RCR has set a priority for FRCR exam candidates. These are as follows:
Priority 1: UK, Singapore, and Hong Kong trainees and NHS contributors.
Priority 2: Other global candidates.
FRCR exam Part I:
What modules does the FRCR Exam part I have?
There are two modules, Anatomy, and Physics. It is advisable to undertake both exams together to save time and travel expenses. There is no difference in attempting the exam in Hong Kong, Singapore, or the U.K. in terms of difficulty level or probability of passing. In fact, the questions across the centers are the same and synchronized in time.
Anatomy module:
- Consists of 100 image-based questions, displayed on ‘practique’
- Due to the limitation on the number of computers available, application selection happens through a ballot system. Hence it is possible to get selected for Physics but not Anatomy.
- There has been a recent increase in the number of centers and therefore this will be less of a problem, in the future.
Physics module:
- Every application for the physics module is generally approved because it is a written exam with 200 (40 x 5) true or false questions.
- There are 40 stems with 5 sub-questions each. Answers are marked on an OMR sheet.
- No negative marking.
What centers are available for part 1 of the FRCR exam?
Currently, the following venues are available:
- UK – Belfast, Birmingham, Crewe, Edinburgh, Glasgow, Leeds, London, Plymouth.
- Cairo- Egypt,
- Hong Kong
- Hyderabad – India
- Singapore
- Malta
What is the ideal time required for preparation for part 1?
For post PG attempts 1 to 3 months are sufficient depending on your work schedule, consistency, and capacity.
What is the strategy for exam preparation and what are some study resources?
Physics
- The best strategy to clear Physics is to read Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging thoroughly, attempt every question and be vigilant about tricky questions.
- Some questions have statements directly quoted from Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging with a small change that alters the whole meaning. If you are not careful you are likely to get misled.
- Most questions are direct but some questions involve applied knowledge and reasoning.
- There is no negative marking and every question should be attempted. As they are true or false questions, you have 50% chance of answer it right, even if you guess blindly.
- Sample FRCR physics question :

- Sample answer sheet:
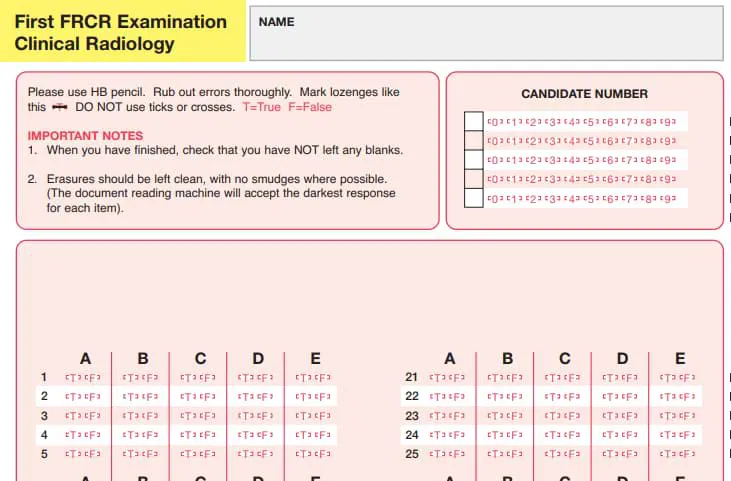
Complete question and answer sheet sample can be downloaded from the FRCR website: FRCR part I physics sample question paper || Answer Sheet.
Recommended resources for FRCR part 1 physics:
Books:
- The physics exam is predominantly based on Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging. If you are attempting the exam after your postgraduate exam and familiar with imaging physics, then reading Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging is sufficient. One or two revisions should suffice. It is a very concise book with less than 200 pages but each line is important. Few questions, especially from MRI and advanced imaging are not covered in Farr’s.
- If you are attempting it as a resident, Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging can be difficult to understand and ‘Christensen’s Physics of Diagnostic Radiology’ can be used as a reference or pre-read before reading Farr’s.
- MCQs for the First FRCR (Oxford Specialty Training: Revision Texts) – by Vardhanabhuti and Gray James is the MCQ book I followed and found very useful and representative of the exam questions. Every chapter of this MCQ book follows that of Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging and it is ideal to do them together.
- FRCR Physics Notes: Beautiful revision notes for the First FRCR Physics exam is also a good resource.
- MRI physics can be daunting. MRI in Practice by Catherine Westbrook is a good book to start with the basics of MRI. You can then read the corresponding section from Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging once you have the basic understanding.
Online resources:
- PassFRCR
- BMJ OnExamination
- R-ITI Radiology – Integrated Training Initiative
- FRCR Physics Notes
- www.mr-tip.com
- FRCRexam.org
- FRCR Scholar
Anatomy
- You will have to answer 100 questions in 90 minutes. So you have less than 1 minute per question. Speed is the key. Try to answer at least 50 questions by the end of 40 minutes and complete the paper in 80 minutes.
- Each question carries 2 marks each and is marked according to the accuracy of the answer. For example:0 – Incorrect answer 1 – Partially correct/less accurate answer 2 – Precise/ accurate answer.
- Do not waste time on a single question. If you are unable to answer a question, flag mark it and come back to it after completing the rest of the exam.
- Each question has an image displayed with one or more arrows. This will be accompanied by a written question usually asking you to identify the structure. However, some questions are about the function of that structure. For example, the nerve supply to the muscle marked or the site of drainage of a duct of the gland pointed. If you simply identify the structure and not answer the question, you will lose a mark.
- Be as specific as possible but not to the extent of making it wrong. For example, if an arrow points to the right hippocampus, you will be awarded full or half a mark if you answer it as the right medial temporal lobe or right temporal lobe. However, if you answer it as Dentate gyrus while the arrowhead points at Alveus you will be marked wrong.
- ALWAYS mention the side. You will lose half a mark if you do not mention it. It is a good habit to always begin the answer by writing the side so that you don’t forget it later.
- Remember that your pass mark is percentile-based and many will score more than 90%. It is a relatively easy exam but even a few mistakes can cost you a lot.
- By the end of the first year of residency, you should have sufficient knowledge to identify most of the radiological anatomy required for this exam.
- Dedicated reading is required in DSA and vascular anatomy, cardiac imaging, MSK images, Barium and IVU studies.
- Familiarize yourself with the practique software before the exam.
- Here is a good guide by the RCR for this: Image-based Exam delivery guide.
- Demo page for the exam: FRCR Demo website. PINs to access the different examinations:
- Anatomy PIN: 501192
- Long cases PIN: 365950
- Rapid reporting PIN: 657439
- The candidate ID number for all three examinations is 11001.
Here are video instructions for the web-based exam platform practique for FRCR part 1 and FRCR Final 2B:
Sample FRCR anatomy questions:
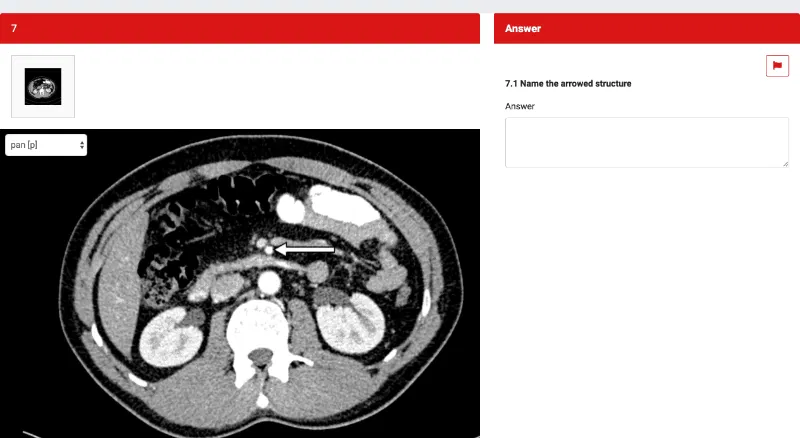
The answer to this question will be”superior mesenteric artery”. A perfect FRCR anatomy answer should always comprise of 3 parts: 1. Side 2. Part of the structure labeled 3. The actual structure (always include the name of the structure and what it actually is (for eg. diaphysis of right humerus bone) Let me explain with an example:
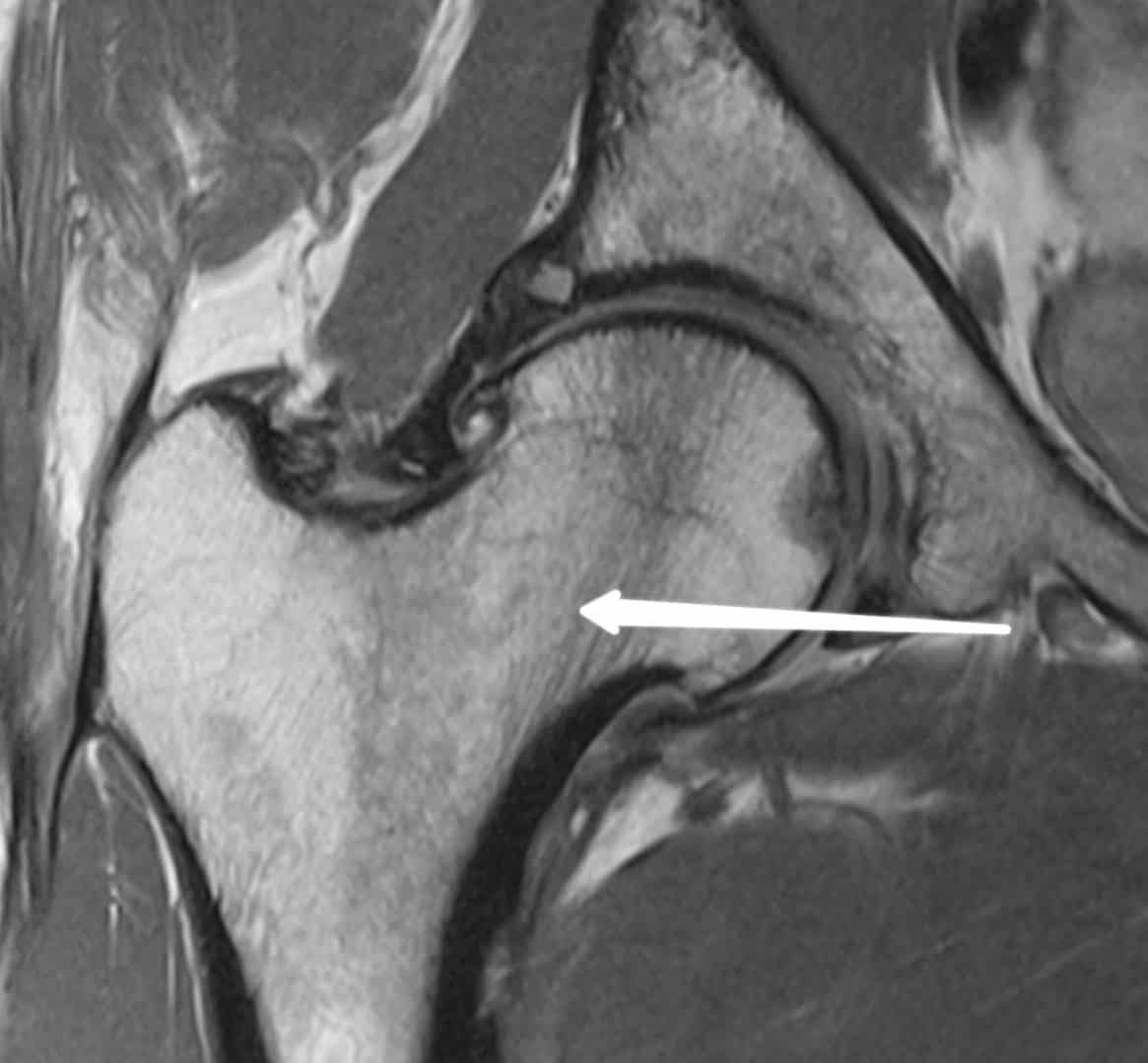
The precise answer for this would be the neck of the right femur or right femoral neck.
- Also, NEVER use abbreviations. For example, answering IVC instead of inferior vena cava may not fetch you any marks.
Recommended study material for FRCR part 1 anatomy:
Books:
- The book recommended is Imaging Atlas of Human Anatomy’ by Abrahams.
- Other anatomy reference books can be found on our anatomy page.
Online resources:
Click on the image below to access our collection of normal anatomy spotters:
Check out the list of websites with free anatomy modules for the FRCR part 1:
- You can refer to the normal anatomy reference guide at RadioGyan.com here: Normal Imaging Anatomy for revising region-specific radiology anatomy. Also, check out this list of commonly encountered normal anatomic variants.
- Radiology Cafe
- Revise Radiology
- FRCR Academy – Great free resource for anatomy cases!
- Anatomy 4 FRCR
- FRCR Scholar
- RadiologyMCQs
- PassFRCR
Are there any in-person courses for the First FRCR Exam?
No in-person courses are available in India. A few courses are available in the UK. These include:
What to do if I have cleared physics but not anatomy?
There is no alternative but to keep applying for an anatomy ballot.
What are FRCR part 1 exam dates for 2022?
The dates are available on the FRCR website.
Part 1 has been updated with edits by Dr. Sandeep Singh Awal.
FRCR exam Part 2A
AKA Final FRCR part A exam
What is the exam syllabus?
The major systems covered are Cardiothoracic and Vascular, MSK and trauma, GI, GU including adrenals, OBGY, Paediatric, CNS and Head & Neck. The RCR provides detailed information on the syllabus and curriculum. : Clinical Radiology Spectrum.
What is the exam structure?
- From December 2017, 2A consists of two papers, each containing 120 single best answer questions (SBAs), across the spectrum. The duration of each paper is three hours, both conducted on the same day.
- Until 2017, 2A comprised of 6 modules, which can be taken together or individually. A total of 6 attempts were allowed to clear all modules. This no longer exists. Even if you are yet to clear only 1 modality you have to complete 2A as per the new exam structure.
What is the strategy for FRCR part 2A?
- RCR has a very good FAQ section on 2A and has all the necessary information about the exam paper. FRCR exam Final part A guide.
- Due to the change in pattern, the MCQ books may not be representative. I attempted 2B in the old format and even then I found the questions that appeared in the exam to be very different from the MCQ books I used. A good understanding of radiology is required to clear this exam and every modality is given equal weightage. Most people find cardiothoracic and MSK to be the most difficult subjects in the exam mainly due to the way we train in India.
- MCQ books can be used as a guide at best, a means to stay focused and to self-evaluate rather than forming a basis for your preparation.
What are the recommended books for FRCR 2A exam?
- SBAs for the Final FRCR 2A (Oxford Specialty Training: Revision Texts): Part 1 and Part 2: –2 books with 600 single best answers each- by Robin Proctor.
- Get Through FRCR Part 1: MCQs and Mock Examination.
- SBAs for the Final FRCR 2A – The Oxford book, by Richard Lindsay : I found this book to be most representative of the exam.
- SBAs for the Final FRCR 2A – The Cambridge book, by Stuart Currie.
- Revision Notes for Final FRCR Part A by Kshitji Mankad.
- If you are reading Grainger and Allison’s Textbook of Diagnostic Radiology, a companion MCQ book is available. I worked out the MCQ book and revised the textbook retrospectively.
What are some online resources for the FRCR part 2A?
- FRCR 2A notes
- Gastrointestinal radiology.
- Genitourinary system.
- Cardiovascular and Thoracic
- CNS and Head & Neck
- Musculoskeletal Radiology And Trauma
- Pediatric
- General Snippets
- FRCR 2A revision podcasts: These are free to download podcasts for the FRCR 2A preparation which you can listen to during commute or when you are too lazy to open your books.
- FRCR exam prep: Over 1200 Final FRCR Part 2A questions with detailed explanations accompanying each answer. You can try their FREE sample question bank before signing up.
When can I appear for FRCR 2A?
The best time is within 1 or 2 years of completing residency.
What are FRCR part 2a exam dates for 2022?
The dates are available on the FRCR website.
Where can I appear for FRCR part 2A exam?
The venues are similar as the first part and include Belfast, Birmingham, Cairo- Egypt, Crewe, Edinburgh, Glasgow, Hong Kong, Hyderabad – India, Leeds, London, Malta, Plymouth, Singapore, Bridgend Wales.
Advice for FRCR 2A exam from Fazel Rahman Faizi, a third-year radiology resident in Kabul, Afghanistan who cleared his FRCR 2A exam in his first attempt:
First, one should start preparing with a textbook like Grainger (unless you are a consultant with lots of experience). I only did Grainger essentials system-based followed by MCQs from that particular system. After that, I revised Crack the core along with its videos which I found it very useful and exam oriented. I recommend revising this book at least two times (the last time one week before the exam). MCQs are useful but do not overwhelm yourself with too many MCQs as the real exam is more difficult and little different from the current MCQ books. Many questions in the real exam were next to step questions and tested the depth of the knowledge. The most useful MCQ books for me was GET THROUGH FRCR 2A and Oxford. Online MCQs were also very useful.
FRCR exam Part 2B
AKA Final FRCR part B exam
What are the components of the final FRCR Part 2B exam?
The Final FRCR (Part B) Examination consists of three scoring components: Two oral exams, a reporting
session, and a rapid reporting session. The resultant sets of marks are considered as a whole to generate a pass or fail. The written components (Rapid reporting and Reporting session) are held on a single day whereas the oral exam is usually held after 3-7 days.
The platform used for the exam is the same as the one used for the anatomy exam. You can check the explanatory video by RCR in the part one section of the blog above.
What is the format and scoring system for FRCR part 2B?
- Rapid Reporting:
You will get 30 images, each with one mark, so a maximum of 30 marks. The total time allotted is 35 minutes. One-third of these cases can be normal. Anatomical variants are considered normal. The rapid reporting component of the exam is marked out of 8.
Here is the marking scheme for Rapid Reporting:
| Image type | Candidate response | Mark |
|---|---|---|
| Normal image | Correctly classified | +2 |
| Incorrectly classified (appropriate false positive) | +1 | |
| No answer given | 0 | |
| Abnormal image | Correctly classified and correctly identified | +2 |
| Correctly classified but incorrectly identified | 0 | |
| Incorrectly classified (false negative) | 0 | |
| No answer given | 0 |
The candidate is marked for each of the 30 cases using the above scheme and depending on their total marks, they get a score out of 8 as follows:
| Total marks | Overall mark |
|---|---|
| 0-48 | 4 |
| 49 | 4½ |
| 50-51 | 5 |
| 52-53 | 5½ |
| 54 | 6 |
| 55-56 | 6½ |
| 57-58 | 7 |
| 59 | 7½ |
| 60 | 8 |
2. Reporting Session (FRCR 2B long cases)
You get six cases and have the opportunity to attain a maximum of 8 marks for each case, so a maximum of 48 marks. Total time allotted is 55minutes for ALL the cases.
Marking system for individual cases. is as follows:
| Candidate response | Mark |
|---|---|
| No answer offered | 3 |
| Fail: significant observations missed; correct diagnosis not made | 4 |
| Borderline: appropriate if there are two main diagnoses in the case but only one is mentioned; some observations missed | 5 |
| Pass: most observations made correctly; principal diagnoses correct | 6 |
| Good Pass: additional relevant material included in a “pass” grade answer | 7 |
| Excellent: a perfect answer, clear and confident | 8 |
Depending on the total for each case, the candidate is awarded a total score out of 8 as follows:
| Total marks | Overall mark |
|---|---|
| 18-25 | 4 |
| 25½-28 | 4½ |
| 28½-31 | 5 |
| 31½-34 | 5½ |
| 34½-37 | 6 |
| 37½-40 | 6½ |
| 40½-43 | 7 |
| 43½-46 | 7½ |
| 46½-48 | 8 |
3. Oral Examination / Viva
This component consists of 2 oral examinations usually in different rooms by 2 pairs of examiners, each lasting 30min and each for 8 marks. In each pair, one examiner will conduct the viva for 15min and the other will score the candidate and they will swap for the next 15min. Thus you will be facing 4 examiners for a total of 60min.
| Performance Description | Comments | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Very poor answer | Key findings missed even with help Wrong or dangerous diagnosis | 4 |
| Poor answer | Slow to spot abnormality Poor differential diagnosis Needed help to get correct answer | 5 |
| Principal findings seen | Some abnormalities seen with help Principal diagnosis correct Limited differential | 6 |
| Good answer | Key findings spotted quickly Correct deductions made and correct diagnosis Good differential offered | 7 |
| Excellent answer – all findings seen | Correct diagnosis and deductions No errors Succinct/accurate report Excellent differential | 8 |
Overall scoring for the Final FRCR Part 2B Exam:
Following the compilation of marks, each candidate will have a score of 4-8 in each component of the examination (two orals, the reporting session and the rapid reporting session). The pass mark in each component is 6, making the overall pass mark 24.
In addition to achieving a score of 24 or above, candidates must obtain a mark of 6 or above in a minimum of two of the four components (i.e. candidates must not have a score of less than 6 in three components). Any candidate not achieving 6 or above in two or more components will be deemed to have failed the examination even if the required score of 24 is attained overall.
Ref: RCR Scoring System
Where should I take this exam?
It is my personal opinion to take the exam in the U.K.
How does the application process work for a U.K. attempt?
- Currently, applications are processed on a first-come-first-serve basis.
- Previously the college followed a ballot system,details of which are as follows:
- Once your application for 2B is approved, your application number will enter a rolling ballot system. Let me explain rolling ballot with a hypothetical situation:
Your waiting list number is 250. Number of slots available is 100. Number of U.K. candidates applying for the current session is 40. Number of slots available to Non-UK candidates will be 100 – 40 = 60. First 60 in the rolling ballot will then be invited. If 20 of them don’t accept the invitation, next 20 will be invited and so on. Once the session is over, depending on the number of non-U.K. candidates who took the exam, your rolling ballot number will get revised. In this example, 250 – 60 = 190.
- Usually, the number of slots available in the U.K. is 250 to 260. But depending on how many opt in or out, candidates with waiting list number as high as 400s might get an invitation. But this comes close to the exam (a few days to 2 months prior). U.K. visa will also take time to process. So unless you prepare in advance, you will end up declining the slot and wait.
- If you sit for the exam and fail, you will have to re-apply and wait all over again.
- At present, it takes a minimum of 1.5 to 2 years to get the slot. So start preparing after 1 year, assuming you will get the next slot.
How does Singapore exam work?
- Singapore conducts a joint FRCR/MMed exam once a year, usually summer. The exam is the same as the FRCR exam but you get an additional degree called MMed (their MDRD equivalent). You have to pay an additional 1.9 lakh rupees for the MMed application. You cannot apply only for the FRCR exam and skip MMed. I am not aware of any benefits of obtaining MMed in Singapore, India or elsewhere.
- Rapid reporting and long cases are the same and synchronized to the exam happening in U.K.
- In Viva, at least two of the examiners are British and the other two are from Singapore.
Where can I appear for FRCR part 2B exam?
Exams are available in Belfast, Birmingham, Bridgend Wales, Cairo- Egypt, Crewe, Edinburgh, Hyderabad – India, Leeds, London, Malta, Plymouth but the venues are variable for each exam session. Kindly check this page for details.
What FRCR 2B courses are available in India?
- Dr. Ian W Turnbull International FRCR 2B Course
- Chennai FRCR course
- Bangalore Columbia Asia FRCR course.
- RITA FRCR Part 2B Training Program
- Bangalore FRCR 2B tutorial day
Are the courses available in India sufficient to clear the exam?
- Courses in India give you a fair idea about the exam and will help in preparation. They are less expensive than courses abroad and you will save on travel expenses also. Few people I know of, have attended only this and cleared the exam. But I strongly recommend you to do at least one course in the U.K. just before your exam.
- The main difference is in the viva practice sessions. In the U.K. courses, there are a number of examiners from the NHS and are not jet lagged. There will be a fair number of local trainees and you will learn as much from them as with the examiners or cases. The way local trainees handle a difficult situation, correct a mistake they have made or discuss a case is different from the way we are used to. Listening to U.K. trainees’ answer at a viva session will help you in the exams.
What are international FRCR courses available?
Most good courses get fully booked 6 months to 1 year in advance so kindly book in advance.
- Revise Radiology
- Red Dot radiology Course
- Edinburgh 2 day FRCR Course
- Edinburgh 1 day FRCR Course
- East Midlands FRCR 2B Course
- East Midlands FRCR 2B reporting course
- Aunt Minnies for FRCR 2B Course
- South West FRCR Courses
- King’s FRCR 2B Revision Course
- Norwich Radiology Academy FRCR 2B Course
- South Thames Rapids Course
- Peninsula FRCR 2B Revision Course
- Heart of England FRCR 2B Revision Course
- Coventry FRCR IIB Course
- FRCR 2B Master Course
- London FRCR 2B Preparation course
How many courses are required before the exam?
At least one Indian course before or during your FRCR exam preparation and one or two U.K. courses before your exam is my personal recommendation. It depends on your level of confidence, experience in radiology and language skills. I attended 3 in India and 2 in the U.K. It is simpler to take an extra course than to repeat the exam.
What are the books available and recommended for FRCR part 2B?
- Accident and Emergency Radiology: A Survival Guide – MUST READ for Rapid reporting.
- Final FRCR 2B Viva: A Survival Guide.
- FRCR 2B Viva: A Case-based Approach
- A Complete Guide to the Final FRCR 2B (MasterPass)
- Rapid Review of Radiology (Medical Rapid Review Series)
- Long cases for the Final FRCR 2B
- Top 3 Differentials in Radiology: A Case Review, Thieme publication
- Chapman & Nakielny’s Aids to Radiological Differential Diagnosis.
- Radiology Review Manual – Dahnert
What is the strategy for Rapid reporting?
- This is the make or break of the 2B exam.
- You have to report 30 cases (mostly radiographs) in 35 minutes. There will be a mix of normal and abnormal radiographs(40 to 60% each) and each pack will reflect an X-ray bundle from trauma referral.
- Online reporting resources:
- FRCR scholar: I found this one to be the best among them. It is a paid course.
- FRCR tutorials by Dr. Sameer Shamshuddin has free packs available.
- Radiology spotters at RadioGyan.com
- Radiopaedia.org Rapids
- Radiopaedia.org Vivas
- CRISP Trust – Part 2B FRCR teaching
- FRCR Longs
- RadioGyan radiology Telegram Group.
- Do at least one or 2 packs a day, every day for one or two months before the exam.
- With good preparation, it is definitely possible for you to get an 8 on 8 in Rapid reporting. This will compensate for any misfortunes in Long cases or viva.
- You will now understand that if you get an 8 in rapids, even a 6 in long cases and 5+5 in viva will earn you a pass. However, if you fail in Rapids, it will take an enormous effort to compensate.
- You will undertake Rapids and Long cases on Day 1 of the exam and viva is spread over the next few days (typically Monday to Friday). A good performance in Rapids is very reassuring (half the battle won!) and that very confidence will help you sail through Viva.
- If you perform badly in Rapids, you will become very anxious and pressurized during your viva and perform badly under stress.
- I gave FRCR 2B twice. Once, in Singapore 2016 when I performed badly in Rapids (score of 5) and ended up failing the exam by 1 mark.
- The next attempt in U.K. 2018 when the former happened. This story is not an exception but the usual scene of most people who fail the exam. Rapids will be your boon or your bane.
Tips for FRCR 2B rapid reporting (RR) by Dr. Nazahat Pasha
In the rapid reporting component of the examination, there is no margin of error. One is certain to fail even with a score of 26/30 in rapid reporting (unless one performs exceptionally well in viva or reporting session).
- It is very important to always follow a comprehensive checklist of all review areas for each body part. It is essential to exclude all expected pathologies in a given radiograph.
- Attempt as many mock examinations or packets (i.e. sets of 30 plain films with approximately 15-17 abnormal films) as possible. More of such exposure will improve your performance in the actual examination by fine-tuning your review areas and developing a habit of looking at the edge-of-the-film abnormality.
- Never forget to look at the side marker, to avoid missing dextrocardia or situs inversus.
- Any pathology in the examination setting has to be definite with no inter-observer conflict (even if subtle). In the examination, you would find most abnormalities easily identifiable. If you are unsure or confused, it is likely a normal film. If you are finding it difficult to detect an abnormality, then the film is likely normal. During the examination, just adapt your routine practice of reporting plain films. It’s a different situation in the examination due to the non-availability of clinical information. This will increase your level of difficulty and may lead to overcalling normal films, which you need to avoid. Imagining abnormalities also must be avoided. Avoid wasting time by not pondering too long over a difficult-to-diagnose film. You should have sufficient time remaining to re-check all normal films.
- If there are multiple views in a case, check them with attention. Such cases are mostly abnormal. Most of the times, the abnormality is evident only in one view. If you don’t have enough time, just mark these type of cases as abnormal.
- If you are short of time, then don’t waste time counting the exact rib number or toe; just mention fracture rib or metatarsal. If you are short of time, it is appropriate to write “#” instead of “Fracture”. Also, it is appropriate to use short forms if you are short of time.
- There is no negative marking in rapid reporting, so you must answer all the questions. During the last few minutes of the examination, if you are short of time, just mark all remaining cases as normal. You have nothing to lose in this scenario.
- Please note that in the actual examination, normal and abnormal cases can be clumped together. For example, if you come across 4 or 5 normal films in a row, don’t be tempted to overcall pathology. Develop a habit of trusting your instincts.
- If you are short of time or are confused about the specific name of a fracture or a radiological sign, then it is appropriate to write a brief description of the abnormality instead of writing a wrong name.
- Most abnormalities in the examination will be relatively easy to diagnose. Most of the films will have a single significant abnormality. Even if there are more than one, it will be part of a single diagnosis (e.g. tibial plateau fracture associated with knee lipohaemarthrosis). If not, then write the most clinically significant one (e.g.: pneumoperitoneum over gallbladder calculi). In rare cases where you find two pathologies like pneumothorax and a lung mass, or osteoporosis and a vertebral wedge compression fracture, or pneumomediastinum with a rib fracture and you are confused, then it is appropriate to write all important pathologies.
- A systematic and consistent approach is a must to be successful in the rapid reporting component of the examination. Apply a uniform technique when attempting mock tests so you can judge your reporting style and know if you are over calling or under-calling the abnormality.
- In case of a fracture extending into an adjoining joint, mentioning intra-articular extension is important to secure a full mark. In skeletal radiographs, always look for soft tissue swelling which may point to an underlying bone fracture. Similarly, foreign bodies and soft-tissue gas may also serve as pointers to significant adjoining abnormality. Always check and trace the outline of each bone in a radiograph with attention. Erosions / foreign body/lines/ tubes should always be specifically looked for.
- A prosthetic valve, laminectomy, calcified hilar lymph nodes, fused vertebrae, splenomegaly, soft tissue calcification except for vascular calcification, severe osteoarthritis, basal ganglia calcification in child etc. are ABNORMAL.
- Basal ganglia calcification in adult, calcified lymph nodes in abdomen etc. are NORMAL.
- In knee, shoulder and skull x-ray films, always look for a fat-fluid level.
- Images are digitized and displayed on OSIRIX workstation
- Normal or abnormal – if abnormal must write down a diagnosis
- Can write with a pencil or pen (both will be provided)
- There is only limited space for the answer, think before you write! (another good reason to use a pencil)
- Abbreviation ok to use – Rt (right), Lt (left), hash sign # (fracture)
- Can get 0.5 if the answer is incomplete
- Only ONE finding per film – if more than one usually related to the same mechanism (e.g. Rib fracture + lung contusion from trauma)
- Normal variant = normal (e.g. Cervical ribs)
- Congenital abnormality = abnormal (e.g. Spina bifida, right-sided aortic arch)
- Expect films with gross fracture – so obvious even medical students can diagnose
- Most abnormal films have unequivocal findings once you spot them
- A small number (? 1-2) of discriminatory films with very subtle findings designed to test good candidates
- RR is likely to break or make you – many good candidates have tripped and fallen over RR over the years. RR should be your top priority – can’t stress this enough. It is the only component of the exam candidates stand a realistic chance of scoring full mark by getting all 30 plain films right – which will give you a lot of room for error in Viva (VV) and Long Case (LC). On the other hand, it’s also extremely easy to screw up RR because of the strict pass mark (27/30) – one tiny mistake may cost you the entire exam!
FRCR Rapid reporting checklist
Craniofacial
- Skull radiograph checklist
- Fracture – depressed
- Sphenoid air-fluid
- Air in orbit and skull
- Sella
- FB in the eye
- Lytic lesions in the skull
- Upper C spine – dens
- Facial bones radiograph checklist
- Fluid in maxillary sinus
- Don’t call blow out – say orbit floor #
- Tripod
- C-spine radiograph checklist
- AA distance
- Harris ring
- Prevertebral soft tissue
- 3 lines
- Fracture – Chance, peg, hangman fracture.
- Facet – perched
- Lumbar and thoracic spine radiograph checklist
- Collapse
- Lung mass / lobar collapse
- Paraspinal soft tissue
- Empty VB sign – each VB should have accompanying posterior elements – vertebra plana
- Pedicles – mets
- SI joint
- Calcified aortic aneurysm
- Chest radiograph checklist
- Situs
- Air: Pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumoperitoneum, surgical emphysema
- Apices – nodule or pneumothorax
- Bones: shoulder dislocation, clavicle fracture, humerus fracture, missing pedicle, check ribs last (missing rib, lytic area, notching, fractures)
- Cardia: heart chamber enlargement, pericardial effusion, retrocardiac region
- Mediastinum – tracheal deviation, paratracheal stripe
- Collapse: veil, retrocardiac triangle, RML, RUL
- Diaphragm: lesion behind the diaphragm
- Hila, mediastinum – esophagus
- Lungs – call it NODULE or consolidation – not mass or pneumonia
- Pleura – CP and cardiophrenic recess
- Soft tissue – Breast shadow, neck mass, axilla (look for clips etc.)
- Shoulder radiograph checklist
- Dislocation or #
- AC joint
- Bankart lesion
- AVN
- Lung – mass, PTX
- Ribs – # or lytic lesion
- Wrist radiograph checklist
- Triquetral fracture on lateral
- Scaphoid fracture will have 4 views
- Hamate hook # on lateral and AP
- Scapholunate dissociation
- Distal radius # – impacted fracture
- Buckle, torus, SH #
- AVN of lunate and scaphoid
- Hand radiograph checklist
- MC or phalange #
- Acro-osteolysis
- Foreign body
- Abdomen radiograph checklist:
- Bones, stones, solid (organs), liquids (bile, urine), gas (extraluminal, mural, intraluminal)
- Bowel – obstruction, hernial orifice
- Foreign body
- Colitis – thumb printing, toxic megacolon
- Pneumo – look if the gas takes the shape of the kidney, Rigler, PV gas or pneumobilia, retroperitoneal gas, GB or urinary bladder air
- Soft tissue – hepatosplenomegaly, psoas outline, kidneys, pelvic mass, missing spleen
- Calcification – aortic aneurysm, appendicolith, gallstone, renal stone, uterine fibroid, dermoid, pancreatic, hydatid
- Bones – sacroilitis, ivory vertebra, missing pedicle, missing VB (collapse), lytic lesion in pelvis, AVN, Lower ribs
- Lung base– bronchiectasis
- Pelvis:
- SI joint
- Avulsions – AIIS, pubic tubercle
- Looser zones
- Iliac wing #
- SUFE, Perthe
- Impacted NOF fracture
- Hernial orifices
- Lower limb
- Knee radiograph checklist
- Lipohemarthrosis
- Tibial plateau
- SONK in femur
- OCD
- Segond and Pelligreni Steida lesion
- Patella alta and baja
- Ankle radiograph checklist
- Tibial, fibular #
- Lateral talar #
- Talar dome – OCD: look carefully in the part overlapping the fibula
- Calcaneal
- Base of 5th
- Tarsal coalition
- Foot radiograph checklist
- Base of 5th vs apophysis
- Lis franc – alignment
- Stress # – periosteal reaction only
- AVN – Freiberg
- Malleolar #
- Lateral talar #, anterior calcaneal#
What is the strategy for Viva?
- A detailed analysis is beyond the scope of this post. Read the initial pages of any of the above books or the RCR website for details about the exam.
Some general tips for FRCR Viva are as follows:
- You should be able to vocalize your thoughts as you are undertaking each case.
- Do not allow long pauses or answer in one or two words.
- The examiner will always try to help you and will NEVER mislead you. He or she will behave like a clinical colleague who has come to discuss a case and not as a radiology professor.
- Always listen to the examiner.
- Even if an X-ray, MRI and Bone scan are of the same patient, each is marked separately. So make sure you state all your findings for each.
- Take every case as a new one, however good or bad your last case has been.
- Practice as much as possible with a friend or faculty and by presenting aloud.
- Prepare a script for common cases. For example, in necrotizing enterocolitis – say that you are not able to see the femoral capital ossification center and hence think that the infant is a pre-term. Describe the mottled air shadow over the colon and say that you are concerned of NEC. Say that you are searching for free air and specifically for a football sign or Rigler’s sign etc. Next, comment on branching pattern of air over liver shadow and state that you are aware that this need not be a poor prognosticator by itself in contrast to adults. Also, say that the visualized lung fields shows/does not show signs of hyaline membrane disease. Ask for the accompanying chest radiograph because you feel that a child with NEC might require explorative laparotomy and because of the high incidence of HMB in preterm, as a part of good clinical practice, you wish to ensure safety during anesthesia.
- Additional information is available in www.rcr.ac.uk → Clinical Radiology →Examinations → First Final FRCR Part B Examination→ Examiners’ reports.
What is the size of the monitor used to display images?
In FRCR 2B Viva, images are displayed on an iMac. Examiner has a separate screen that is not visible to the candidates. The images we see will appear on OsiriX software. A single apple mouse is shared by both examiner and the candidate. Pan, zoom, window options are available to us. However, it is good etiquette to ask the examiner before changing the window.
Does the mouse used to have a central wheel for scrolling?
No. It is an Apple Magic 2 without a central wheel.
Do they use a Windows-based system for practice or use an Apple workstation?
Rapids and Long cases are windows based Pratique software. Dell or HP or a similar system/monitor. A regular wired mouse such as Logitech is available and so is a keyboard to type in the answers.
Do they give a warning before time is up for reporting?
Yes. Periodic warnings are given in both written modalities. A clock display is also projected.
What are FRCR part 2b exam dates for 2022?
Check the available venues, fees and dates here: FRCR Part 2B final Exam Dates
Sample cases for the FRCR 2B
Check a few sample FRCR 2B viva cases courtesy Revise Radiology telegram group:
Mock Viva and tips For FRCR Final Exam by Dr. Sameer Samshuddin:
Subscribe to our YouTube channel for more radiology videos
List of few sample rapid reporting cases:
- Supracondylar fracture
- Scaphoid fracture
- Metacarpal base fracture
- Calcaneum fracture
- Metatarsal stress fracture
- Prox phalanx fracture
- Mid phalanx Pathological fracture.
- Humerus greater tuberosity fracture
- Right hilar nodule
- Neck of femur fracture
- Lateral tibial condyle fracture
- Sacral fracture
- Left colitis
- Mandible fracture
Long cases:
- Brown tumor
- PTLD, PKD, intussusception
- Solitary Rib lesion
- Schizencephaly, absent septum pellucidum
- Neurofibromatosis 2
- Cholangiocarcinoma with primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Rapid Reporting
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
- Pituitary macroadenoma
- Left hip pain in child
- Right ankle pain
- Left hydronephrosis
- Esophageal clot
- Upper lobes pneumonia
- Unilateral ILD
- Cervical facet lock
- AVM
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- Pneumomediastinum
- Endometriomas
- Achalasia
- ILD and PTH rib notching
Source: Final FRCR 2B Radiology
How to Crack All 3 Steps in Single Attempt:
Click here to watch the video with Timestamps for each part on the YouTube app. And while you are there, do not forget to subscribe to the RadioGyan YouTube channel for more radiology resources!
Social Groups for FRCR preparation:
- FRCR physics group on Telegram
- FRCR 2A group on Telegram
- FRCR 2B tips and tricks Facebook group
- FRCR 2B tips and tricks Telegram group
- FRCR 2B tips and tricks WhatsApp Group (due WhatsApp’s limit for members this one is full. You can try to join)
- RadioGyan WhatsApp group, Telegram channel, and group: Not specifically for the FRCR but for radiology cases and resources
These will help you be regular with your preparation as most of these groups are currently very active with daily cases/questions. The downside is that most are managed by one individual each and they may or may not continue to post regularly in the future. If you know of any active social media page/group for FRCR preparation, do share it in the comments section.
More FRCR exam resources:
Additional resources :- RCR Junior Radiologists Forum examination guidance FRCR exam guidance
- Radiology Cafe:
- FRCR exam 2B advice.
- CafeRoentgen:
- Passing the FRCR exam 2B
Final words:
I deeply appreciate Dr. Amar Udare for the wealth of knowledge and effort he invests into the website–RadioGyan and his helping nature which drives him to do this. I would like to acknowledge the constant support and friendship of Dr. Ulhaas Shankar Chakraborty throughout our residency and FRCR journey. All the best to each one of you! Remember
Making of the FRCR blog
- We started off asking what exactly you all would like to know. We got an overwhelming response.
- Knowledge about FRCR:
- List of question contributors:
- Pranav Mahadevkar
- Dilip Vincent
- Vijay
- Praveenkumar
- Sithantha Seelan
- Saumil Pandya
-
Sreelakshmi.R
- Anusha Racherla
- Amal Ahmed Alawi
- Khalid Javed
- Khalid Javed
- Rajat Singhal
- Ruchika Singh
- Ali Jiwani
- Resham Singh
- Snehil Kumar
- Akhter
- Adnan Syed Anwar
- Shyamnath G
- Sandeep Singh Awal
- Allahrasan
- Sarath S
- Pooja Narwani
- Mohammed Khaleel Ahmed
- Karri Bhanu Sudeep Reddy
- Dr Saifullah
- Akbar Shareef
- Vineet Kumar
- Sravan Krishna Reddy
- Sreenivasa Raju N
- Himanshu Pruthi
- Sunil Bharatrao Borade
- Shazra Batool
- Arif Abubaker
- Jarvis Pereira
- Dr Syed Inaamullah
- M Tishore Kumar.
- M Tishore Kumar.
- Shubham Singhal
- Shion
- Haritha Chodiboina
- Parameshvar Lal Sharma
- Alok Yadav
- Hana Qudsieh
- Prajakta Patil
- Chamala Rudrateja Reddy
- Lakshay Mehta
- Harsh Lathiya
- Shruthi P
- Kusuma
- Sriharish
- Rajat Agarwal
- Bunty Hotchandani
- Sujan Thapa
- Anshuman
- Rumana Parvin
- Abhishek Verma
- Dr Shankar Poudel
- Elizabeth Joseph
- Akanksh Chokkapu
- Surekha
- S.Baranitharan
- Md Sadaquat Ullah Khan
- Taraprasad
- Renuka
- Renuka
- Shameema Farook
- Sriharish
- Kaustubh Madurwar
- Nishaa P
- Vijayasree
- Vijayasree
- Dwiti Dongara
- Thomas Devasia
- Thomas Devasia
- Rajiv Vanka
- Hirdesh Sahni
- Amilu Elsa Varghese
- Rupinder
- Faraaz Shariff
- Sunaina Dhawan
- Amar
- Komal Pal
- Pravin
- Karthick Subash S
- Gomathiponshankar
- K E Vijay Kumar Gowd
- Kaushik Chakraborty
- Shelina Merlyn
- Mohammad Imran
- Dr Rameez Ghouse
- Pavan Kumar
- Arun
- Jafer
- Srikanth Reddy
- Sanchita Bhawalkar
- Hadiya Begum
- Latiar Hossain.
- Ankit Darediya
- George Roy
- Sayan Sarkar
- R Janani
- Lohit Shivashish
- Ashish Aravind
- Shamika Wagh
- Sri Sai Lakshmi
- Abdul Salam
- Joe
- Meena
- T Seetam Kumar
- Rajcee Chhajed
- Andaleeb Haider
- Dr Akshay Chikar
- Dr Nani
- Rafee
- Akshay Chikar
- Ashish
- Sonalika Jha
- Pawan Rao
- Dr Tameem Ahamd
- Chetan K K
- Roshni A
- Jomon Sunny
- Sachin L
- Dr Chethan Kumar M
- Subinay Saha
- Hemanth
- Rishabh Aggarwal
- Anusha
- Work with Dr Inthulan on Trello.com
- After multiple drafts and edits its finally done !
More Radiology resources: Radiology resources – RadioGyan.com Disclaimer: Every effort has been undertaken to assure the authenticity of the information. However, the essence comes from the author’s personal experience. The Royal College promptly replies to any questions asked and will be in accordance with the latest information. In case of doubts, do email them and update the forum. This is ONLY a guide to help you get basic information. Candidates are advised to check the FRCR website and the websites mentioned in the above post for the latest information. The FRCR logo is for representative purposes only. The RCR is not affiliated to this website.


















Wow it is amazing , thank you so much sir . It is much clear now .
Thank you. Glad that helps !
Thanks a lot
That was indeed a comprehensive sum up of the mystery behind FRCR examinations. Thank you so much Dr. Inthulan Sir and Dr. Amar Udare Sir for the valuable tips and guidance.
Thank you Dr Greta.
Glad we could help!
Very informative blog, thanks for the efforts and sharing your knowledge
You are welcome Dr Ruchi.
Glad that we could help. Keep reading and leaving feedback!
Share with your friends and colleagues as well.
Thanks for ur nice writing.
Very much grateful for your effort.
I am a Bangladeshi citizen. As far I know, there is no such mentor/teacher who can certify me as a FRCR part 2A candidate fulfilling the requirements u mentioned above.
Would u please tell me what should I do for the training required for FRCR.
How can I get trained in UK?
Any idea, please.
Hi Dr Shalah,
Unfortunately we have no information in that context.
amazing explanation which i did not find anywhere online , great job thanks a lot for detailed step by step information
You are welcome Dr Madhu. All credit goes to Dr Inthulan for the detailed explanation.
Do share the page with your radiology colleagues!
Thank you for the precise information sir.
Sir can u also guide regarding career opportunities after clearing FRCR ?
Thank you Dr. Sreenivasa. We have mentioned that in the article above: Questions 12 to 15 in the Introduction section
Could you please guide?
What should one after obtaining DMRD with 24 months training in one institution do to receive 34 months training to sit for final FRCR, what options are available in India to receive the extra 10 months training?
Thanks
George Joseph
Hi Dr George. A few people have asked this query and we are not sure what is the take of the RCR on this. You can try mailing the RCR and find out. If you let us know anything do let us know. We will update that in the blog post.
Thanks
Excellent guide for FRCR exam sir, sir what if we do Post diploma dnb after DMRD can we appear for FRCR part 2B?
Thank you Dr Asif. Yes you can appear for DMRD after DNB.
Amar, you are doing great work bro.
Went through some spotter sets and other info. Keep it up, my best wishes.
Thanks a ton. Just trying to help radiology residents as much as possible
Great blog…that answers most of the queries related to FRCR.
Sir could u please tell what are chances of getting a job in UK under NHS after clearing FRCR..n how tough is it getting GMC registered…considering the time n money we need to invest in the course
Thank you, Dr. Vani. I am not aware of what are the chances of getting a job in the UK and the current procedure for registering for GMC. Someone who is actually working there will be better be able to tell. If I can find that information I shall surely update that.
Thank you so much
This is one stop information for FRCR which is most simplified and most clearly explained .Thanks a ton to Dr Inthulan Thiraviaraj and double ton thanks to Dr Amar Udare sir for this wonderfully trimmed website.
Thank you.
Glad that we could help!
Thank you for a very informative blog.
Kindly explain why it is a disadvantage to take the FRCR exam in Hong Kong or Singapore. I thought it was the same standard as the UK counterpart?
And with the current waiting list in the UK isn’t it worthwhile to try one’s luck at getting a shot at the exam at the other venues?
its great
Thanks a lot
does having 1 year senior residency after DMRD qualifies for part 2B?
That is a question frequently asked.
Unfortunately, I do not know the correct answer. As said above “You can attempt Part 1 and 2A. However, you require 34 months of supervised training, in a teaching college to apply for 2B. Hence with 24 months of DMRD alone, you will not qualify for 2B.”
The best thing would be to mail RCR and confirm with them so that we have an official statement.
If you get to hear back from them, do let us know.
Thank you 🙂
Hi, This blog is a great effort!
I wanted to ask how many attempts are allowed to pass a single FRCR module or examination? I read somewhere on RCR website 6 attempts are allowed, are these 6 attempts in total for all, part 1 physics and anatomy modules, FRCR 2A and 2B examinations, or 6 attempts separate for each FRCR module/ examination? 6 for physics, 6 for anatomy, 6 for FRCR 2A and 6 for FRCR 2B?
Many thanks.
Hello Sir, Thank You So Much For The Blog And All The Information. My Question Is, Is CESR Mandatory Even After Clearing FRCR For Getting A Job In UK ? And Also In Other Countries Like Gulf And Singapore Is FRCR Enough To Work Or Is Any Other Exam Required ?
Hi sir, if we do additional 10 months training after DMRD or DMRE (cps). Are we egligible for FRCR?
As you told us to send RCR a mail, any official update on this? Anyone who has sent this mail to RCR ? Please inform us!
Can we do frcr post dmre(cps)?
I am not sure. You may have to confirm that with the RCR.
Thank you.
Thank you for the extensive guide sir. Just wanted to know, which of the following options is the fastest route to get a breast radiology fellowship in the uk and then practices in the u.k. after???
A. IELTS then PLAB then FRCR
B. IELTS then FRCR
C. OET then PLAB then FRCR
D. OET then FRCR
ive read some articles before , suggesting to do PLAB first to…does it make sense?
This is my current status:
Finished my 4year radiology training in 2018 in the philippines.
Passed my radiology diplomate exam in Jan.2019
Also finished my 1 year ct-mri fellowship last feb.2020 in the same country.
currently reviewing for ctmri subspecialty on july 2020.
Dear Jenri,
Glad that you like the post. Unfortunately, I am not aware of the answer for this. Maybe someone who has taken any of the above routes may be able to help you!
You can try our telegram group where there are other radiologists who may have an answer to this question: https://t.me/radiogyan
Thanks.
Hello sir. This is very informative guide. I have done 2 years of senior residency in government medical college post DMRD . And like you said I have emailed RCR regarding the eligibility. But they haven’t answered clearly. They sent an email attachment where they have stated that 34 months of supervised radiology training.
But it is still uncertain that wether I am eligible or not.
Dear Anand.
The RCR is your best bet. I am not sure if anyone other than them can provide an authentic answer.
Apologies.
-A
Hello Dr Anand, can you send that email attachment to us? Please tell your email address or contact.
I have similar Question, can we do FRCR after DMRE. Please, help.
Thank you for sharing informaton
Welcome!
Dear Sir
Can you tell me if I can apply for FRCR part 1 and 2 once I clear MBBS with one and two years of radiology training?
Hey, Sathish
I think we have answered this question in the video on the page. Here is the link: https://radiogyan.com/guides/frcr-exam-guide/#frcr-exam-tips-video
CAN STUDENTS WHO HAVE JOINED DMRE AT PRIVATE DIAGNOSTIC CENTER RECOGNISED FOR FIRST TIME FOR CPS GIVE PART ONE EXAMS ???
You will have to confirm that with the RCR.
FRCR 1 physics is also computer based exam now instead of paper exam. Solving 4 to 5 MCQ books is must. Physics paper is tougher than the MCQ books available.
Exam bookings procedure has changed significantly wherein slots for entire year open at the same date. This can be found on RCR site.
Anatomy – Get through by Mair is a very good book with good conventional / Xray and USG questions.
FRCR2 A – Lindsay and Grainger MCQ books are very good and close to exam questions in toughness. Crack the core is very good book as a base. Apart from systems, few questions will be from intervention and nuclear medicine. Exam bookings procedure has changed significantly for 2 A too.