Imaging of Adenomyosis (Case-based approach) | Radiology Board Review Case
Clinical features and pathophysiology
- Ectopic endometrium in myometrium AKA endometriosis interna.
- Adeno (glandular proliferation) + myosis (myometrial hyperplasia)
- Can be diffuse or focal (adenomyoma).
- Seen in premenopausal multiparous women.
- Postulated due to invagination of the endometrial basalis layer into the myometrium
- Presentation: Dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, and abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Treatment:
- Hysterectomy – Definite treatment.
- NSAIDS
- Menstrual-suppression hormonal therapy
- Danazol (oral or IUD [intrauterine device])
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist
- However, hormonal therapy for adenomyosis is usually less effective than that for endometriosis because of the differences in hormonal responses of the ectopic endometrium, which is of the basalis type in adenomyosis.
Ultrasound features of adenomyosis
- Diffuse, sometimes globular-shaped, uterine enlargement
- Diffusely heterogeneous myometrium.
- Asymmetrical thickening of the myometrium.
- Indistinct hypoechoic areas
- Myometrial cysts.
- Poor definition of the endometrial-myometrial border.
- Focal tenderness elicited when scanning over the uterus
- Subendometrial echogenic linear striations
- Subendometrial echogenic nodules
- Venetian blind” or “rain shower” appearance
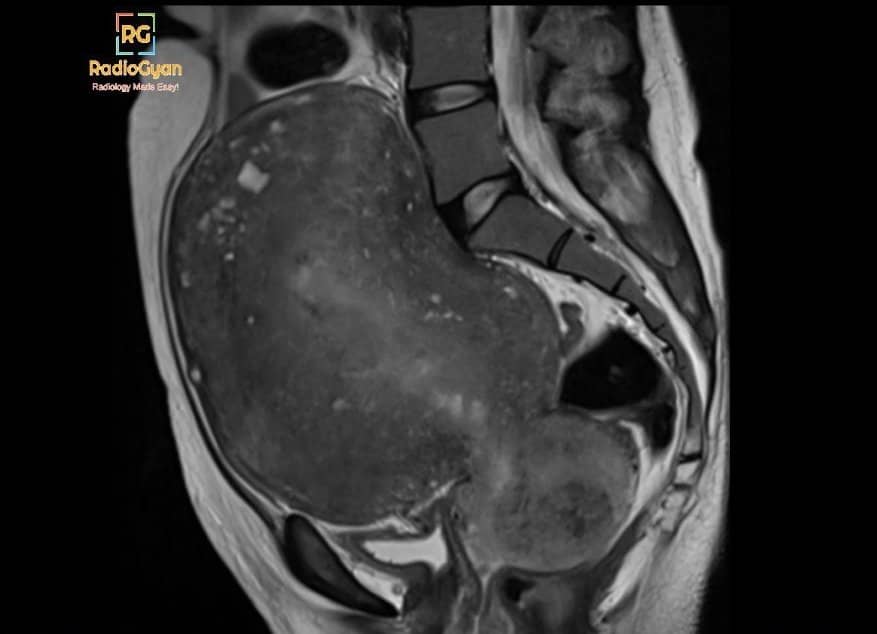
MR features of adenomyosis
- Bulky globular uterus.
- Thickened junctional zone -⁉️_ mm (Watch the video for the exact criteria)
- Ill-demarcated low-signal-intensity area on T2-weighted images owing to abundant smooth muscle proliferation.
- T1/ T2 hyperintense subendometrial cysts at the junctional zone.
- Look for fibroids and endometriosis.
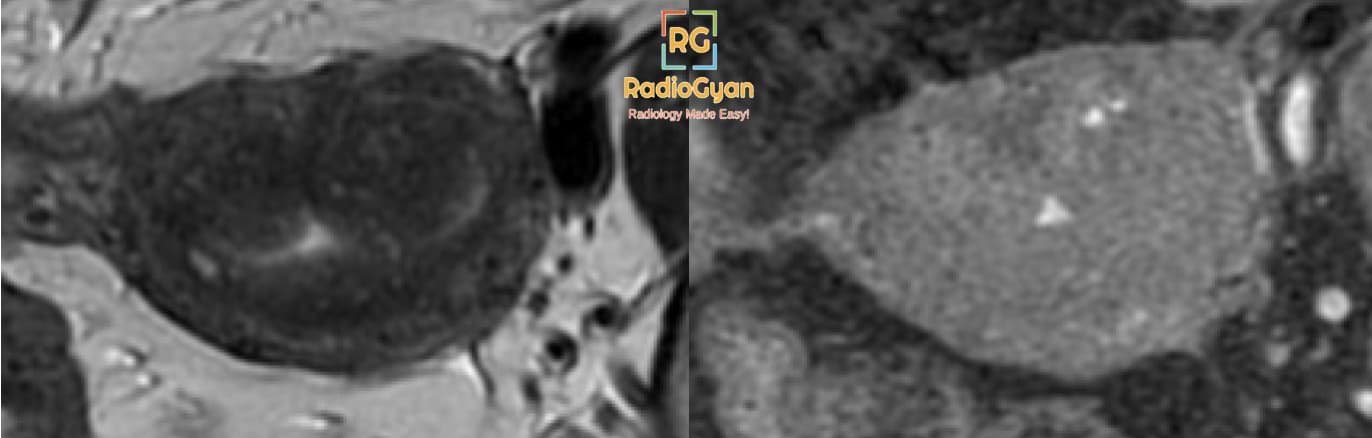
Imaging features of adenomyomas
- Polypoid mass protruding into the cavity.
- It can be treated with surgery, unlike adenomyosis.
- Ill-defined T2 hypointense lesion.
- T1 hyperintense foci.
- Associated with tamoxifen therapy.
How to distinguish adenomyosis from fibroid (leiomyoma)
| Features | Adenomyosis | Uterine leiomyoma |
|---|---|---|
| Margins | Poorly defined Junctional zone | Well circumscribed |
| Appearance | Focal or diffuse | Focal |
| T2 appearance | Small T2 hyperintense cystic foci | T2 hypointense. No cystcs |
| Thickened junctional zone | Yes (>12mm) | No |
| Mass effect on endometrium | Minimal or none | Usually present |
Reference and further reading
To attend live, join our Telegram group to get regular updates for these webinars:
More Radiology videos: