Summary of the video:
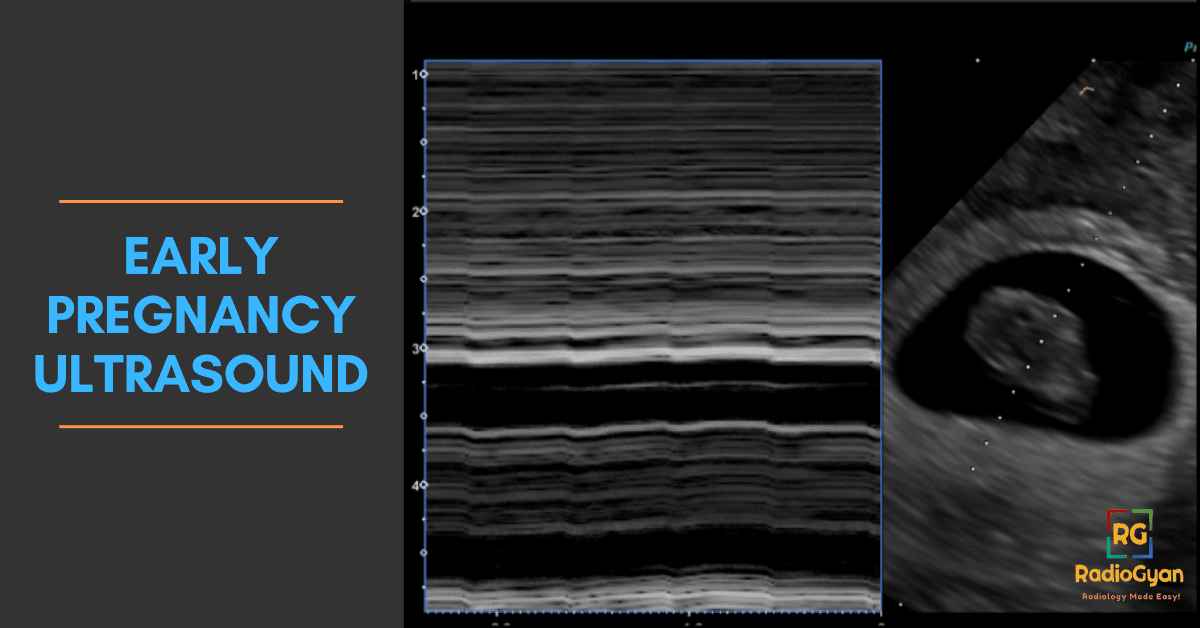
Normal Progression in Early Pregnancy
- 5-6 Weeks: Sequential visualization of endometrium, gestational sac, and yolk sac.
- Signs of Normal Early Pregnancy: Presence of a small fetal pole and appropriately sized gestational sac.
Evaluation of Early Pregnancy Failure Criteria
- Diagnostic Criteria: Crown-rump length (CRL) above 7mm without a detectable heartbeat, mean sac diameter equal to or exceeding 25mm without an embryo.
- Follow-up Recommendations: After two weeks to confirm diagnostic findings and assess for progression.
Read this detailed article for NEJM criteria for early pregnancy failure:
Criteria for Early Pregnancy Failure – NEJM and SRU
Findings Indicative of Poor Prognosis
- Irregular Gestational Sac: Possible sign of intracavitary hemorrhage.
- Large yolk sac.
- Small Gestational Sac: Cramped appearance indicating limited space for fetal development.
- Large amnion
- Bradycardia: Fetal heart rate below 90bpm suggesting a poor prognosis.
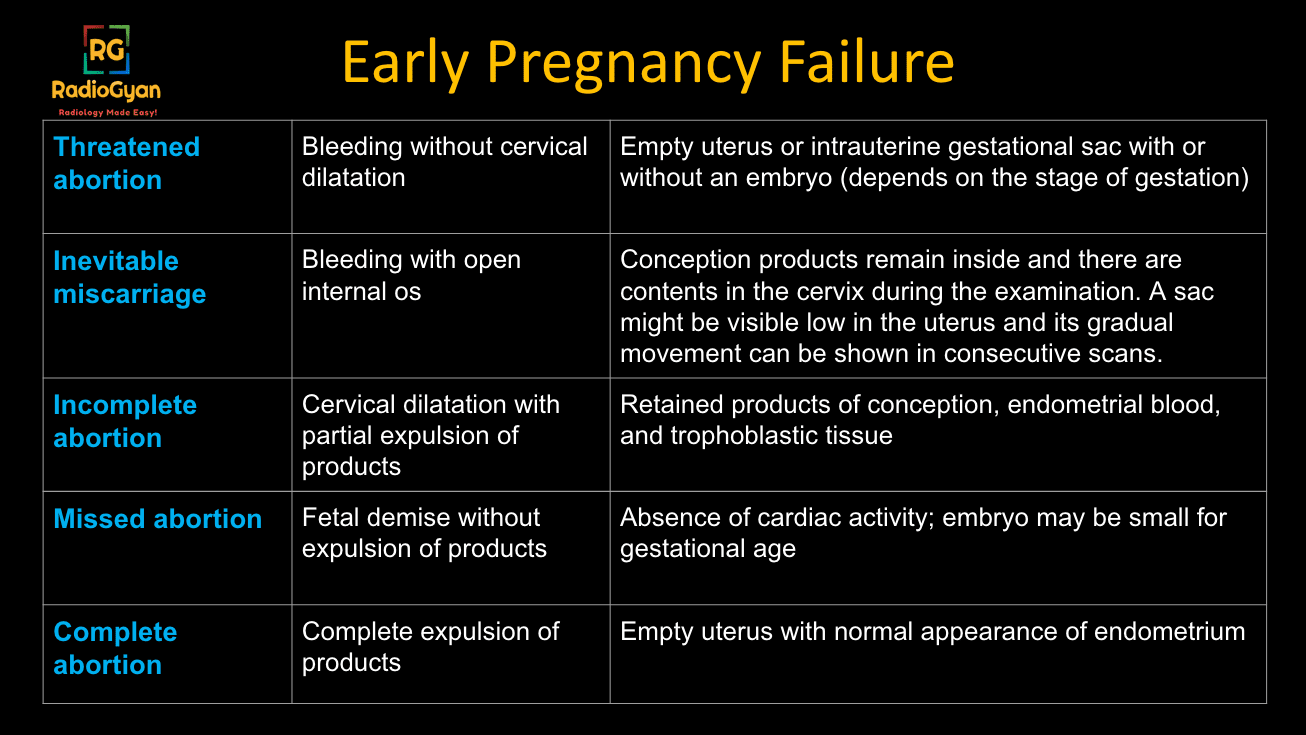
Miscarriage (Abortion) and its types
Retained Products of Conception (RPoC)
- Ultrasound Features: Thickened heterogeneous endometrium, presence of an endometrial mass.
- Differential Diagnosis: Considerations include arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), RPoC, polyps, or submucosal fibroids based on imaging characteristics.
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Spectrum
- Benign vs. Malignant Conditions: Benign entities such as complete and partial moles characterized by elevated beta hCG levels.
- Ultrasound Characteristics: Snowstorm or cluster of grapes appearance within the endometrium indicative of molar pregnancies.
Important Differential Diagnoses and Diagnostic Considerations
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Absence of an intrauterine gestational sac with a separate adnexal mass warrants consideration for ectopic pregnancy.
- Differentiating AVM from RPoC: Utilize Doppler vascularity to distinguish between arteriovenous malformations and retained products of conception.
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Evaluate for cystic changes and persistent elevation in beta hCG levels to differentiate from other conditions.
Key Points for Accurate Diagnosis
- Location Confirmation: Distinguish between intrauterine and ectopic pregnancies for appropriate management.
- Viability Assessment: Evaluate critical parameters such as CRL and sac size to determine pregnancy viability.
- Dating Precision: Importance of accurate dating for timely intervention and decision-making in early pregnancy complications.