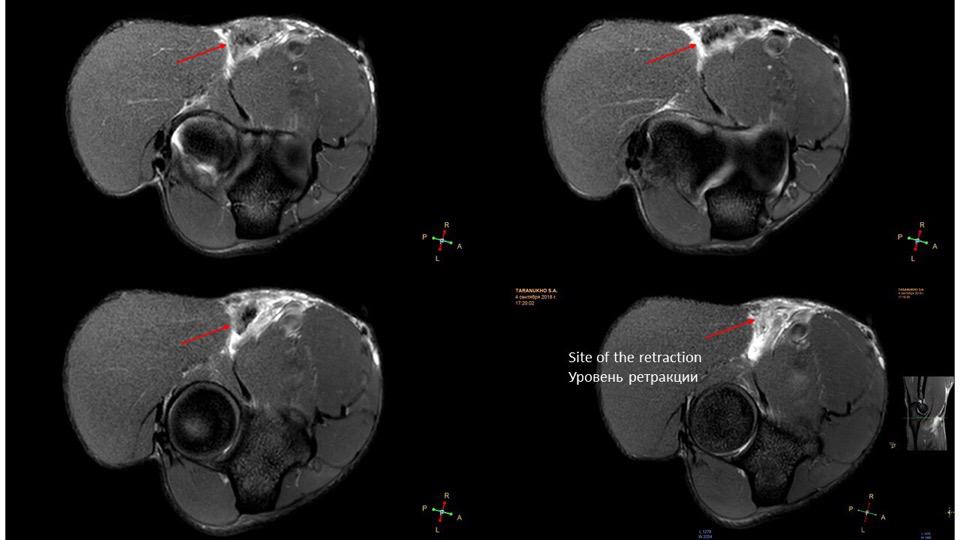
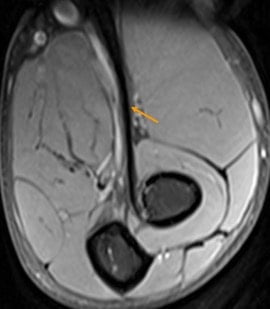
Elbow. Male, 31 years, acute pain and swelling after work out. Full-thickness tear of the distal biceps tendon. MR images showing retracted biceps tendon fibers (arrow) surrounded by edema. Note the thickened distal triceps tendon (asterisk) as a result of chronic overuse.
Biceps brachii distal tendon rupture:
Clinical Features:
- Most commonly in the dominant arm of males after the fourth decade.
- Most tears occur 1–2 cm above the radial tuberosity as this is a hypoperfused zone.
- Complete tears are evident clinically however, differentiation between complete and partial tears is difficult.
| Complete Tear | Partial Tear |
| Single traumatic event involving large force acting against resistance from an elbow flexed to 90° | Minor trauma or not even associated with a traumatic event when the underlying tendon is degenerated) |
| Usually acute | Usually chronic presentation |
| Hook test does not elicit pain. “Popeye sign” | Hook test elicits pain |
| Discontinuity with or without retraction | At least some fibers are intact |
| Surgical management | Conservative to start with. |
Ultrasound:
- Dynamic imaging can be used to evaluate continuity of the tendon or the abnormal movement of a disconnected proximal tendon.
- Partial tears show changed caliber with reduced echogenicity which is often difficult to evaluate.
- Posterior acoustic shadowing at the distal biceps has proven to be highly sensitive for a full thickness tear.
- Anisotropy at distal tendon end can mimic complete rupture.
Tendon retraction of less than 8 cm correlates with an intact aponeurosis, whereas a retraction of more than that indicates torn aponeurosis.
MRI
- Fluid-signal filled gap on STIR sequence, increased intratendinous signal intensity, and edema in the biceps muscle belly and surrounding soft tissues are characteristic for acute full thickness rupture.
- Partial tears show altered signal and caliber of the distal biceps tendon.
- FABS view: Flexed ABducted Supinated view is superior to routine imaging for evaluation of the distal biceps tendon.
Associated pathological conditions:
- Enthesophyte formation at the radial tuberosity which also can be a contributing factor.
- Bicipitoradial bursitis.
Differentials:
- Brachialis muscle sprain.
Further reading:
- RadCases MSK
- USG of Biceps tendon rupture
- Radiographics: Distal Biceps tendon pathology
- RadSource.
- Radiology Assistant
Case courtesy: musculoskeletal_rad_cases
More radiology content at RadioGyan : Radiology resources