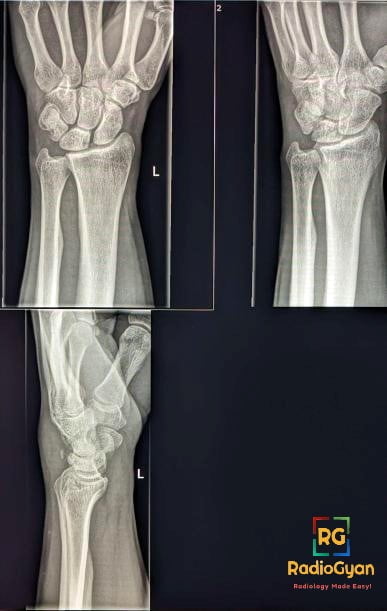
Quiz
What is the most common mechanism of this fracture ?
- Blunt trauma to the wrist
- Fall from height
- Fall on the outstretched hand
- Penetrating trauma to the wrist
Pathophysiology
- Triquetrum is the second most commonly fractured carpal bone followed by scaphoid.
- Dorsal cortical fracture being the most common type of triquetrum fracture.
- Fall on the outstretched hand with wrist in extension is the most common cause of fracture
- Various mechanism involved in causing the fracture include impaction by ulnar styloid or hamate, avulsion by the dorsal radiotriquetral or dorsal scaphotriquetral ligaments.
Key Imaging Features
- Radiography– Dorsal cortical fractures are best evaluated on the 45-degree pronated oblique and lateral views- avulsed bony fragment seen posterior to the triquetral bone
- CT- To rule out occult triquetral fractures with high clinical suspicion.
- MRI – In suspected carpal instability to look for extrinsic carpal ligament injury and bone marrow edema in occult fracture.
Imaging Recommendation:
Radiograph with AP and lateral view or CT \ MRI for suspected occult fracture
Top Differential Diagnosis:
- Os triangulare- accessory ossicle between ulnar styloid, lunate and triquetrum
- Pisiform fracture- pisiform fractures are uncommon and 30 degrees supination view is required to visualise a pisotriquetral joint.
Clinical Features:
- Symptoms- ulnar-sided wrist pain worsening on wrist flexion and extension, dorsal wrist swelling and tenderness over the dorsal aspect of the triquetrum
Classification System:
Classification system developed by Garcia-Elias to differentiate the patterns of dorsal cortical fractures
Type 1 -nondisplaced- most common type
Type 2 -partially displaced at the proximal end
Type 3 – partially displaced at the distal end
Type 4 -completely displaced fragment
Type 5 -multiple completely displaced fragments
Type 6- fracture line through the coronal plane in which the dorsal side is displaced
Etymology and synonyms :
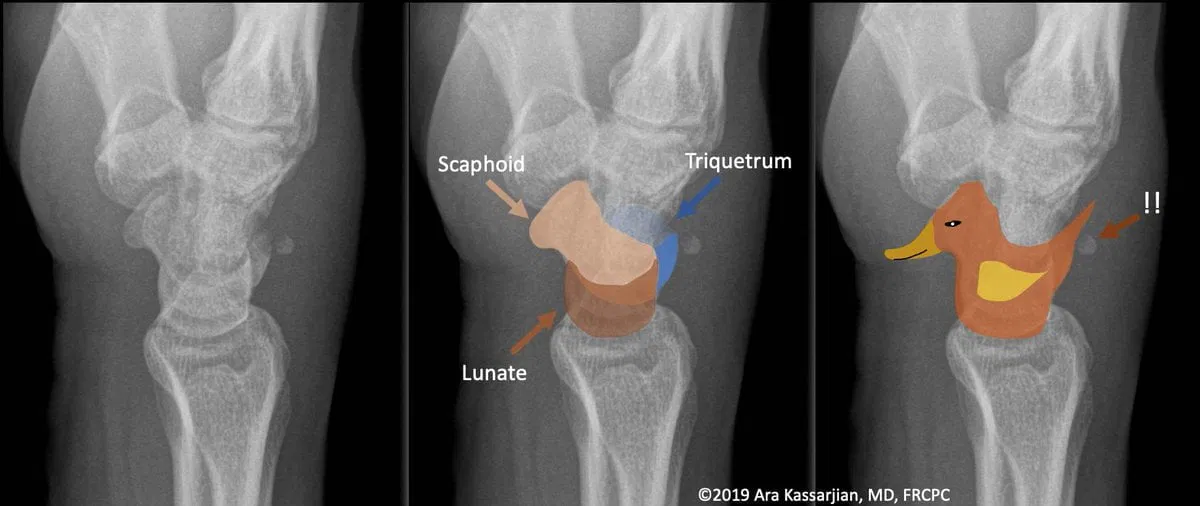
The pooping duck sign derives its name from the resemblance of the combined outline of the scaphoid, lunate and the dorsal portion of the triquetrum to a duck and the avulsed triquetral fracture fragment to a poop from the duck.
Treatment:
- Non-surgical management – immobilisation for 4-6 weeks
- Surgical management- presence of significant displacement of the fracture fragments or fracture-dislocation concerning for instability
References:
Single best review article:
Case co-authored by TeamGyan Member Dr.Mansi