Quiz
There is increased risk of retained products of conception in case of:
- Advanced maternal age.
- Vacuum assisted delivery.
- Placenta accreta.
- Past history of Cesarean section.
Pathophysiology
Persistence of intrauterine tissues formed after conception beyond the termination of pregnancy is known as retained products of conception. Microscopically it is diagnosed based on the presence of chorionic villi.
Key Imaging Features
- Ultrasound ( gray scale):
- Increased endometrial echo complex. (8 to 13 mm)
- Intrauterine mass.
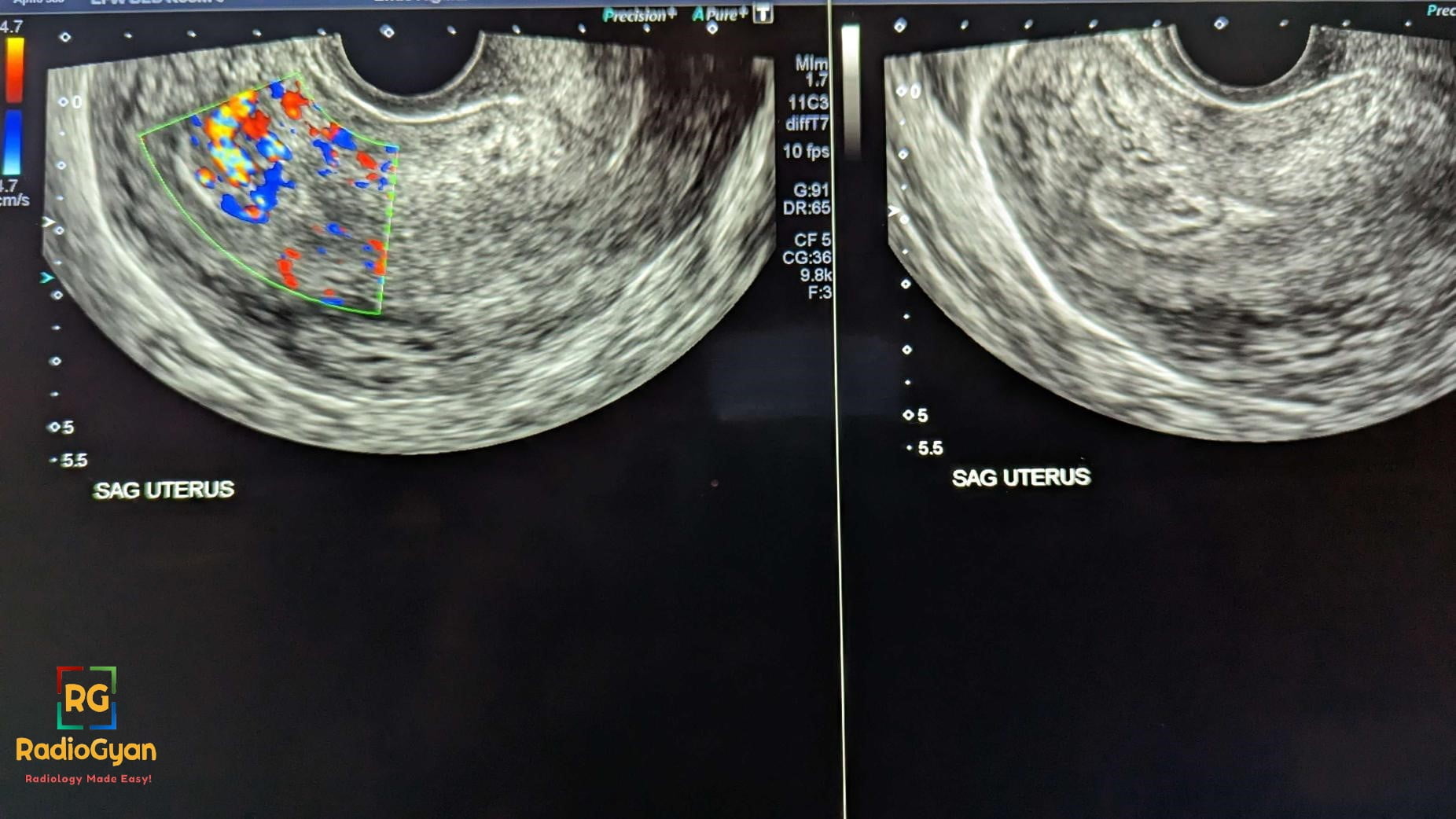
- Doppler:
- Vascularity seen from myometrium extending towards endometrium. ( not isolated to myometrium)
- Absence of doppler has low negative predictive value ( RPOC can be avascular)
- The degree of vascularity of the intrauterine component can be compared with the myometrial vascularity in the same image section and graded as type 0, 1, 2, or 3.Refer Gutenberg classification for more details. A schematic representation is as follows:

- MRI/CT:
- Intracavitary uterine soft tissue.
- Variable myometrial thinning, junctional zone obliteration.
- Post contrast enhancement within the endometrial cavity.
- T1, T2 characteristics majorly depend on the extent of necrosis and hemorrhage within the RPOC.
Imaging Recommendation:
Grayscale and doppler ultrasound as first line modality. MRI is suggested for complicated cases.
Top Differential Diagnosis:
- Blood clots- No vascularity.
- Uterine arteriovenous malformation – Vascularity in the myometrium.
- Uterine lesions like endometrial polyp or submucosal fibroid.
- Subinvolution – rare entity.
- Invasive hydatidiform mole.
Clinical Features:
- Symptoms :
- Bleeding:
- Primary(within first 24 hours) postpartum hemorrhage.
- Secondary (bleeding after more than 24 hours upto 6 weeks) postpartum hemorrhage.
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Fever.
- Bleeding:
- Age predilection: More common with advanced maternal age.
- Risk factors if any :
- Placenta accreta.
- History of RPOC in previous pregnancy.
- Advanced maternal age.
- Instrumental delivery.
- Second trimester delivery/miscarriage/abortion.
- Arrest during delivery/ Prolonged labor > 14 hours.
- Prolonged oxytocin use.
- Nulliparity.
- Past uterine surgery.
- Congenital uterine anomaly.
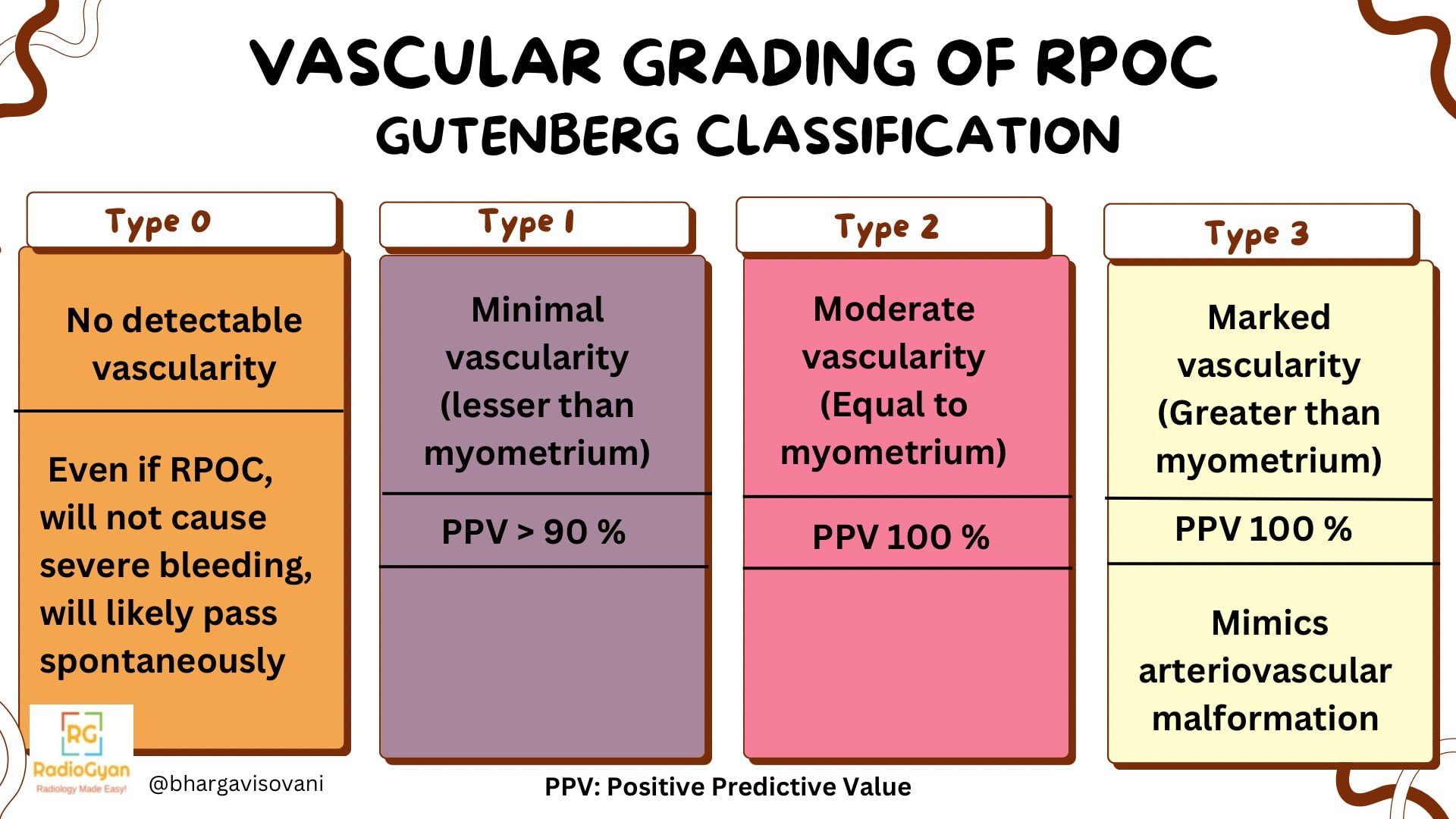
Classification System:
The Gutenberg Classification is a system used to categorize Retained Products of Conception (RPOC), which are fetal or placental tissues left in the uterus after a pregnancy. This classification system includes three types:
Type 0: Hyperechogenic avascular mass
Type 1: Different echoes with minimal or no vascularity
Type 2: Highly vascularized mass confined to the cavity
Type 3: Highly vascularized mass with highly vascularized myometrium
Treatment:
- Medical: Misoprostol.
- Surgical: Dilatation and curettage.
References:
- Sellmyer, M.A. et al. (2013) “Physiologic, histologic, and imaging features of retained products of conception,” RadioGraphics, 33(3), pp. 781–796.
- Pacheco, L.A. et al. (2019) “1809 hysteroscopic management of retained products of conception: The New Gold Standard?,” Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology, 26(7).
- Retained products of Conception (RPOC): Causes, risks & treatment, Cleveland Clinic. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21512-retained-products-of-conception (Accessed: 07 August 2023).
Case co-authored by TeamGyan Member Dr. Bhargavi Sovani