Quiz
Which of the following syndromes is NOT associated with Fibrous dysplasia?
- McCune Albright syndrome.
- Mazabroud syndrome
- Jaffe-Lichtenstein disease
- von-Hippel Lindau syndrome.
Answer: Von-Hippel Lindau syndrome is not associated with fibrous dysplasia.
Pathophysiology
Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a benign bone disease wherein osteoblasts do not normally differentiate, leading to immature bone and fibrous stroma.
Key Imaging Features
Slide the image for an annotated image.
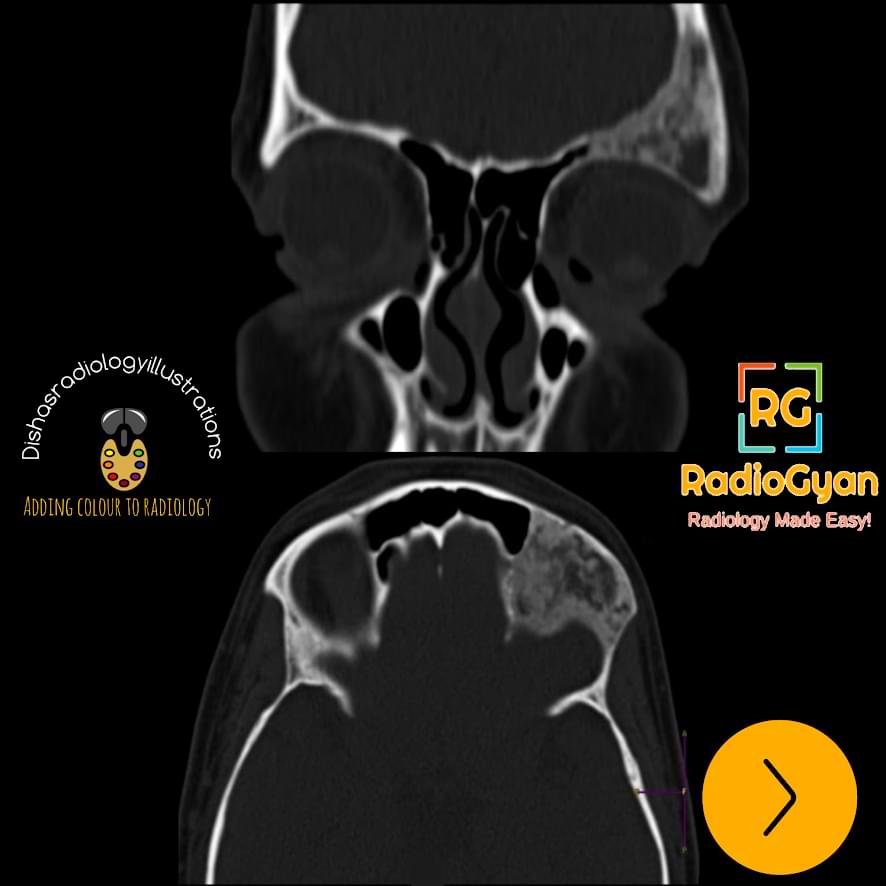
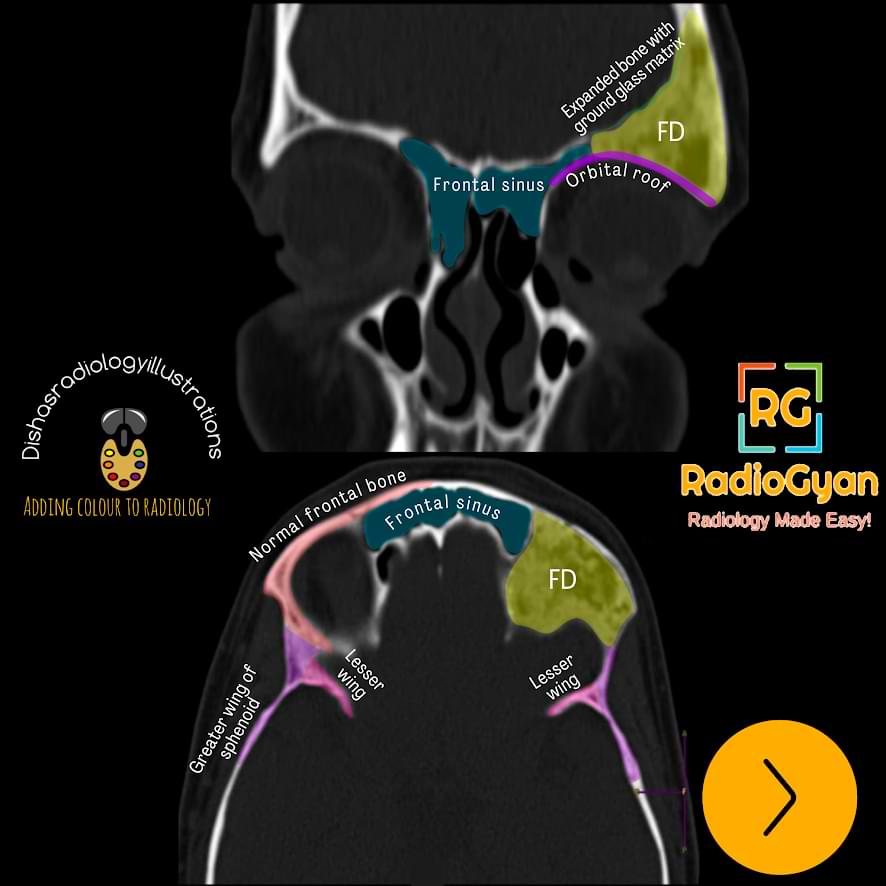
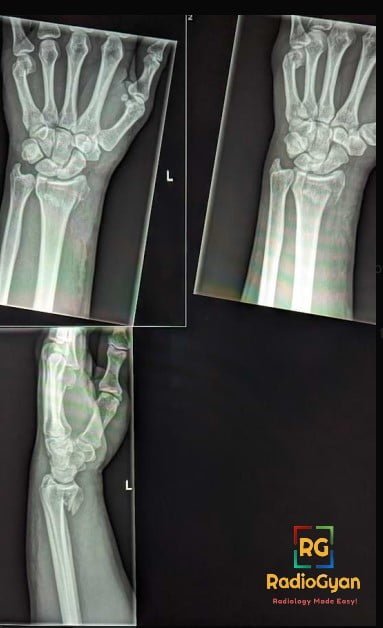
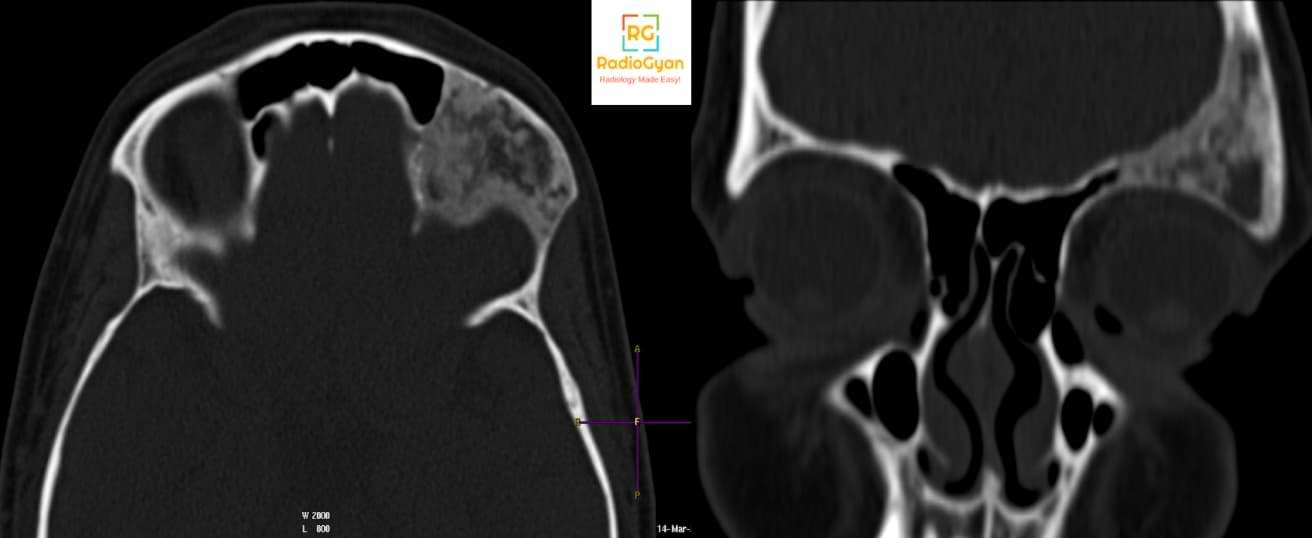
Radiographs:
- Intramedullary, well-defined expansile lesions.
- Cortical contour is smooth.
- It may show endosteal scalloping.
- On conventional radiographs, they appear ‘ground glass’ or hazy, few may be radiolucent or sclerotic.
- A thick layer of sclerotic bone around the lesion is classic – known as a rind sign
- The absence of periosteal reaction is typical.
Fibrous Dysplasia can have a lucent appearance on radiographs and is a part of the FEGNOMASCHIC group of lesions.
FEGNOMASCHIC is a mnemonic for the differential diagnosis of lytic bone lesions. It stands for,
F -Fibrous Dysplasia
E -Eosinophilic granuloma and Enchondroma
G -Giant cell tumour
N -Nonossifying fibroma
O -Osteoblastoma
M-Metastases and Myeloma
A -Aneurysmal bone cyst
S -Solitary bone cyst
H -Hyperparathyroidism (brown tumours)
I -Infection
C– Chondroblastoma / Chondromyxoid Fibroma
Alternatively you can use this mnemonic : FOGMACHINES as it is easy to remember.
Fibrous Dysplasia
Osteoblastoma
Giant Cell Tumor
Metastasis / Myeloma
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Chondroblastoma / Chondromyxoid Fibroma
Hyperparathyroidism (brown tumors) / Hemangioma
Infection
Non-ossifying Fibroma
Eosinophilic Granuloma / Enchondroma
Solitary Bone Cyst
CT Features:
Typical ground-glass appearance as seen on radiographs.
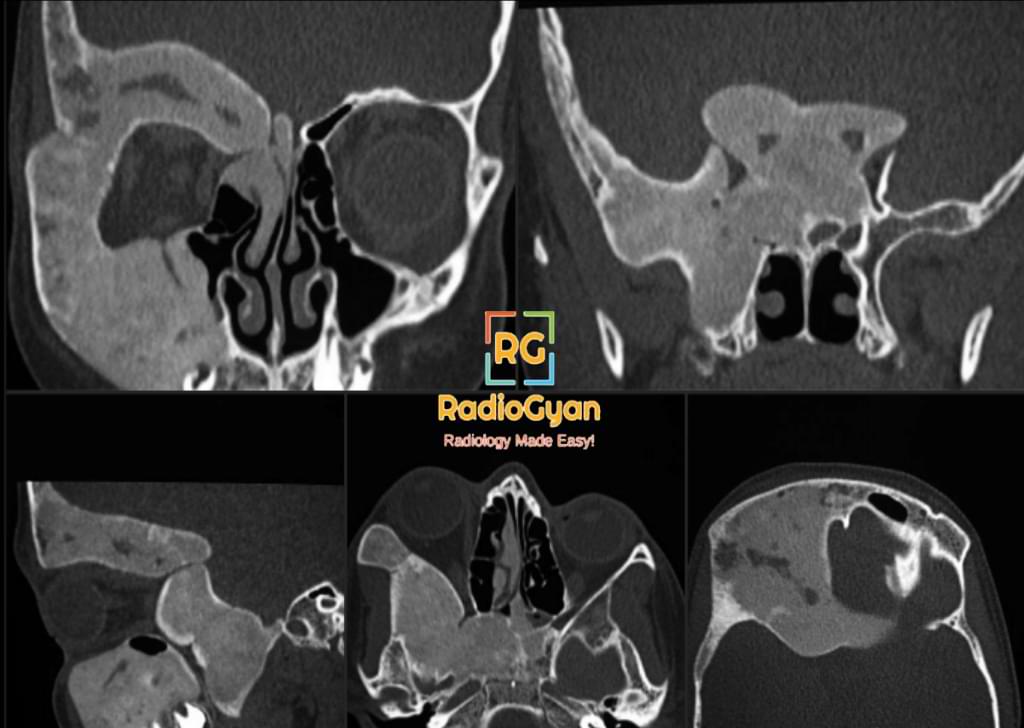
MRI features :
- Intermediate to low intensity on T1- weighted images, intermediate to high intensity on T2 – weighted images
- Heterogeneous enhancement after contrast administration. Diffuse enhancement can give rise to “milk cloud” appearance.
- MRI appearance can simulate an aggressive lesion.
Nuclear Medicine:
Non-specific increased uptake is present in these lesions on radiotracer scans.
Imaging Recommendation :

Radiographs are sufficient for diagnosis in most cases. CT can be performed in selective cases for confirmation. Best to avoid MRI as it can show an aggressive appearance.
Top 3 Differential Diagnosis :
- Pagets disease: Cortical sclerosis and thickening is seen in Paget’s, which is absent in FD.
- Jaffe-Campanacci Syndrome
- Triad of nonossifying fibromas, axillary freckling, and café au lait (lacks neurofibromas).
- Can simulate polyostotic forms of FD. However, the café au lait in J-CS is like the Coast of California, while those in McCune-Albright resemble the Coast of Maine.
- Neurofibromatosis: Osteitis fibrosa cystica in NF can mimic FD, but there will be other findings of NF.
Clinical Features :
- Symptoms: may be an incidental finding or can present with pain and compression over adjacent structures( especially in craniofacial disease- there is compression of nerves exiting neural foramina of the skull base)
- Age/Sex predilection: monostotic disease may present in 2nd or 3rd decade, and polyostotic presents in children
- Progression:
- Age-related changes: with an increase in age, there is decreased number of cells in the lesion , changing the classic radiographic appearance of ground glass to a more dense and sclerotic pattern.
- Treatment-related changes: Bisphosphonates cause the development of parallel sclerotic metaphyseal bands. (These bands develop in any growing child treated with bisphosphonates and are not specific to FD)
- Complications: pathological fractures, malignancy,benign changes like arachnoid bone cyst formation and myxoid changes.
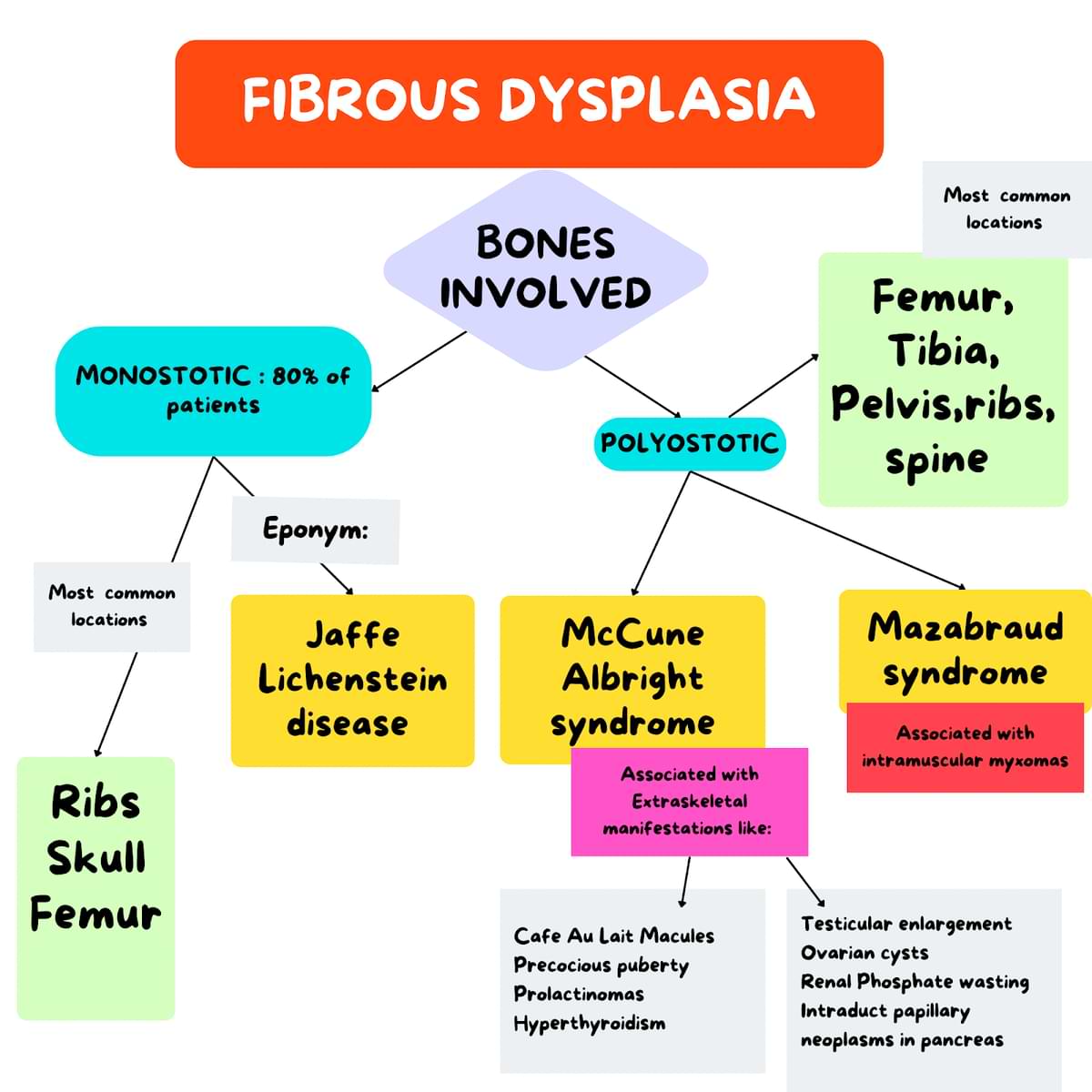
Classification System :
- Monostotic – 80% AKA Jaffe-Lichtenstein disease.
- Polyostotic – 20% McCune-Albright syndrome: UNILATERAL FD associated with extra-skeletal abnormalities,
- Mazabraud syndrome: FD with associated intramuscular myxomas.
Etymology and synonyms :
- Marrow is replaced by fibrous tissue, hence the name fibrous dysplasia.
- Also known as osteitis fibrosa and osteodystrophy fibrosa
Treatment :
Symptom management, endocrinology evaluation in case of polyostotic form. Surgery is reserved for aggressive symptomatic cases, especially in craniofacial dysplasia.
References:
Single best review article:
Other references:
Co-Authors: Dr. Bhargavi Sovani. Illustration by Dr. Disha Lokhandwala.