Quiz
All the following are features of this pathology except?
- Ataxia
- Nystagmus
- Memory loss
- Action tremors
Pathophysiology
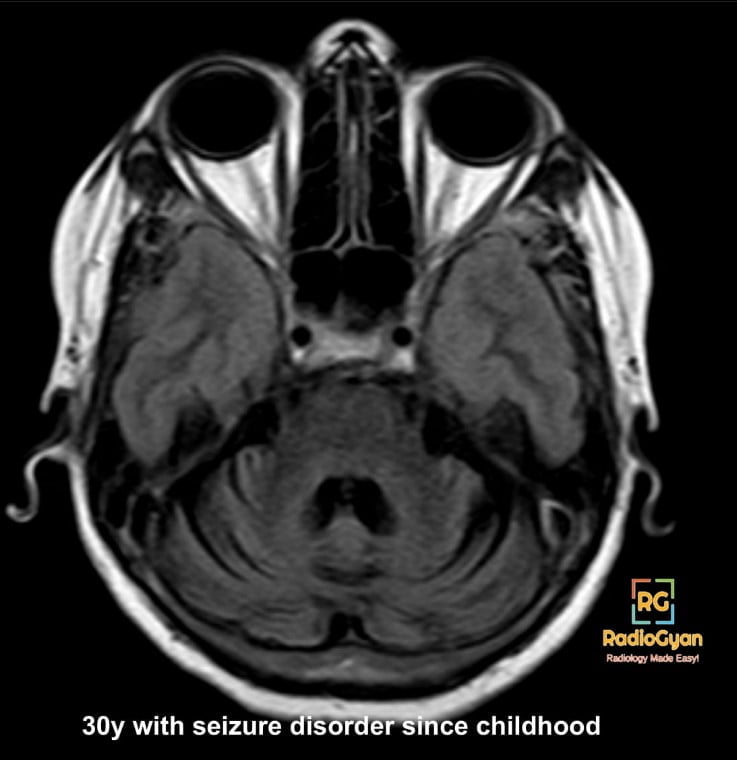
Phenytoin is used in the management of epilepsy, generalised tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Phenytoin blocks the voltage-dependent sodium channels This will increase the membrane threshold for depolarization and ultimately lower the neuronal cell susceptibility to epileptogenic stimuli. The neurotoxic effects of phenytoin are concentration-dependent. Phenytoin may cause cerebellar degeneration with the destruction of the Purkinje cells and a reduction in the granule cells with Bergmann gliosis and relative sparing of basket cell axon of the cerebellum
Key Imaging Features
- Diffuse pan-cerebellar cerebellar volume loss
- Calvarial thickening
- Enlargement of 4th ventricle and basal cisterns
- MR spectroscopy is more sensitive in detecting underlying cerebellar dysfunction even before the appearance of structural abnormalities. MR spectroscopy shows a reduction in the NAA/Cr ratio which states underlying tissue biochemistry and underlying structural changes such as a reduction in the number of neurons while cerebellar volumetry shows cellular loss over time.
Imaging Recommendation :
MRI brain plain scan to evaluate the size, and shape of the cerebellum and associated features
Top 3 Differential Diagnosis:
- Alcoholic cerebellar degeneration– Cerebellar atrophy, vermian atrophy and Wernicke encephalopathy
- Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration is associated with small-cell lung cancer, ovarian malignancy, breast carcinoma and Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Cerebellar hypoplasia- Reduced cerebellar volume with preserved shape. Stable appearance over time.
Detailed clinical history will help in diagnosing the cause of cerebellar atrophy.
Clinical Features :
- Symptoms – Ataxia, cerebellar dysfunction, hypotonia, nystagmus and action tremor.
- Age/Sex predilection —
- Risk factors- Phenytoin exposure for longer duration or higher doses, previous cerebellar injury. The hepatic CP450 enzyme system metabolises phenytoin(CYP2C9 and CYP2C19). Patients with CYP2 mutation and drugs that alter the function of increasing the plasma phenytoin concentrations (eg- amiodarone, cimetidine, cotrimoxazole, disulfiram, fluconazole, metronidazole, chloramphenicol, sodium valproate, 5-fluorouracil, and sulphonamides).
Treatment:
Phenytoin discontinuation
References:
Single best review article:
Other references:
- Algahtani H, Shirah B, Alqahtani AJ, Al-Malki AQ. Irreversible Cerebellar Atrophy as a Complication of Short-Term Phenytoin Exposure: Clinical Improvement Following Discontinuation of the Culprit. J Epilepsy Res. 2020;10(2):96-99. Published 2020 Dec 31. doi:10.14581/jer.20016
- Gupta M, Tripp J. Phenytoin. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; July 11, 2022.
- Shanmugarajah PD, Hoggard N, Aeschlimann DP, et al. Phenytoin-related ataxia in patients with epilepsy: clinical and radiological characteristics. Seizure. 2018;56:26-30. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2018.01.019
Case co-authored by TeamGyan Member Dr Gauri Parvathy, Edited -Dr. Mansi