The National Board of Examinations recently changed the examination format for DNB examinations and introduced OSCE. OSCE stands for Objective Structured Clinical Examination, a method of assessing clinical competence in medical education.
An OSCE involves completing timed activities (OSCE stations) in a simulated or actual clinical environment, with trained examiners using standardized scoring sheets to assess performance.
Common categories of OSCE stations include clinical examinations, communication skills, data interpretation, simulation/ABCDE assessment, and clinical procedures. The number of OSCE stations and their length vary across different medical schools and year groups.
In this article we share a few tips to ace this new format of the DNB Radiology Exam.
How to study for the DNB Radiology OSCE Exam?
The best way to prepare for the DNB OSCE is to select one or two sources (eg. RadioGyan spotters and OSCE, Telegram group created by Dr. Sanjay Yadav, RadCases , etc) that have a mixed bag of cases and do not try to use too many books. Usually, the duration given to prepare for the practical is limited and trying to do too many things will only create panic.
- Before you start using any source, write down a list of all the systems, so that you can make sure you do not miss at least the important cases from each system.
- Count how many days you have before the exam and make sure you cover all the systems (mainly important cases) over this period, because when you use larger resources like Rad cases, you may not finish all the books on time.
- Whenever you see a case, read the typical points about that case, for example: gender and age predilection, associated syndromes, named radiological signs, etc.
- Make sure you see at least a few images of every fluoroscopic procedure, as the first question is these cases will be “name the procedure” and you should not end up wasting time on this question.
- While using the Radiogyan OSCE, make sure you bookmark the cases you got wrong or where you exceeded the time limit, so that you can go through these the day before the exam.
- Similarly, if you are using telegram groups to see cases, make a separate chat where you can forward the cases that you got wrong.
- Do not forget to solve at least 10 to 15 statistics cases (Sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV) and perform the calculation mentally with a 4 minute timer. In the exam, you do not have any space for rough work and the questions are usually very long so you have to be very quick with the calculation.
- Go through basic parameters of all modalities, especially those that are displayed on the corners of a CT, MRI and ultrasound image (eg. mechanical index and thermal index for bone).
NOTE : No single resource will cover EVERY case and therefore, when you see a case, make sure to look at images of all differentials of the pathology at the same time. For example : you see a case of acoustic schwannoma —- also see CP angle meningioma, epidermoid, etc.
How to prepare yourself before DNB Radiology OSCE exam begins?
The first part of the DNB practical examination is the OSCE. All candidates are seated in a room with a projector and are handed 20 answer sheets (one for each OSCE station). This usually happens 30 minutes prior to the start time, so that the candidate has enough time to write their roll number on each sheet.
- When you are allotted a seat, make sure the screen is clearly visible from where you are seated, and if your view is obstructed, inform an invigilator immediately.
- This will be your seat throughout the exam and you do not have to change seats for each OSCE.
- Carefully write your details on each sheet but keep an eye on the clock as you will not get time to do this once the OSCE begins.
- Count the sheets handed to you and make sure you have the correct number.
- Keep an extra pen ready because the OSCE cannot be paused by invigilators at the centre. It is being displayed all over the country simultaneously so any issues at your end will cost you time.
- Stay calm and make sure you are comfortable as there is only one break in the entire duration of the OSCE and this is the most scoring part of the exam.
- If at any point during the exam there is a display issue, do not panic, the invigilators will take note of it and if any cases are missed at your centre, provisions are made at the end of the exam.
- DO NOT use the back of the answer sheet as only one side of the sheet is scanned and sent to national board.
- After the OSCE begins, there will be only one break (after half the stations are over), so it is very important that you address any issues with the invigilator before the OSCE starts.
- There will be 15 seconds between questions for the invigilators to collect papers. Do not continue writing at this time as the examination is under video surveillance and it is possible that the invigilator collecting the sheets might also be the examiner for your viva.
What to expect once the OSCE starts?
Each OSCE station is projected on a screen with a timer. You have to write the answers for that station on a single sheet (which you were given earlier). Once the timer ends, the sheet is taken from you and then the next OSCE will be displayed on the screen and you take a new sheet.
Here is a sample DNB Radiology OSCE Sheet

- Some OSCE stations are split into 2 parts and this will be indicated on the screen — be attentive as the timer will also be set accordingly and split between the two slides. You will have to answer both the parts on the same sheet.
- I noticed during my exam that many of the cases had a very long clinical history which took time to read. While the history can be useful, I suggest take a good look at the image first as you can just glance over the history for key words.
- As mentioned earlier, questions pertaining to statistics are especially long and reading them takes up a good chunk of the 4 minutes, so if you have not practiced these earlier, it might be difficult during the actual exam.
- Whenever you write your answer, do not forget basic things like laterality (right or left), do not use short forms and answer to the point. There is no time to write long answers.
- If you are really confused between two answers, take 10 seconds and think about what you are going to write because the sheet is taken away from you after the timer ends and you cannot change these answers later.
Radiology OSCE Cases Examples
A few types of questions that are commonly asked during DNB Radiology Exams :
- Name the study.
- What are the findings?
- What is the diagnosis?
- What are the other types of this disease?
- Name some benign and malignant lesions having a similar appearance.
We have compiled a list of 25 such common question types for DNB Radiology OSCE exam. Share your email below to download a PDF list of these commonly asked questions:
An example Radiology OSCE case is shared below.
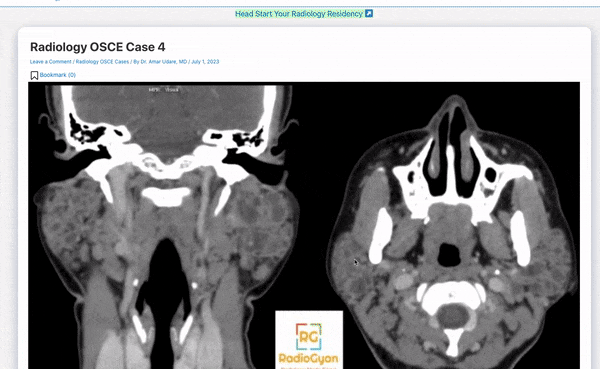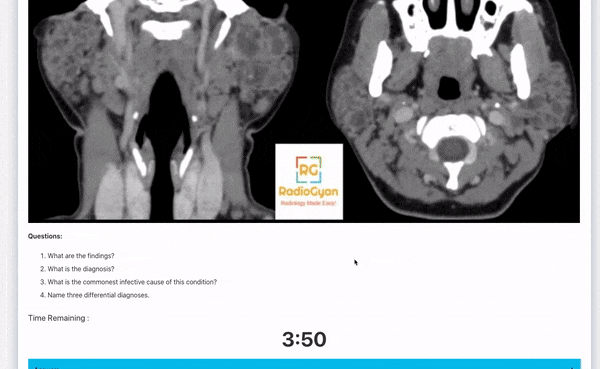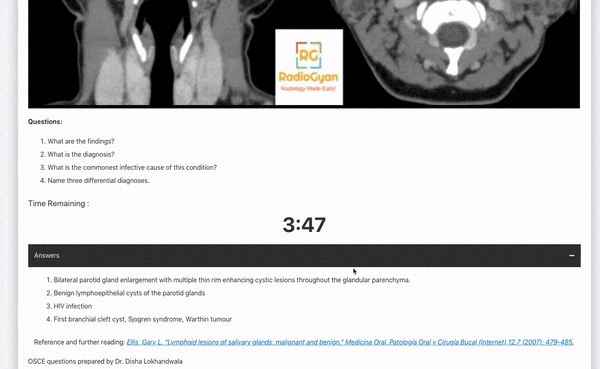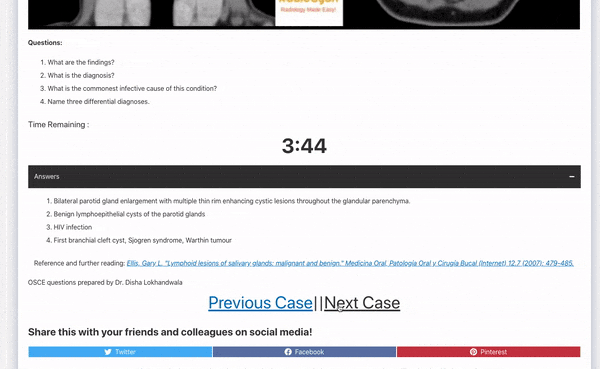
You can check out more such Radiology OSCE cases on this page:
While the OSCE seems stressful, I actually felt it was the most scoring part of the exam as it is completely objective. Do not stress about seeing each and every case during your preparatory period as that is physically impossible. Focus more on common pathologies and trust the work you have put in for the last 3 years.
Good luck!
Dr. Disha Lokhandwala
DNB Radio-diagnosis



The DNB Radiology OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination) is a critical assessment for radiology residents in India pursuing their Diplomate of National Board (DNB) qualification. It’s designed to evaluate candidates’ clinical and practical skills in radiology. DNB Radiology OSCE comes from a combination of knowledge, practical skills, and effective communication.
This article by Dr. Amar Udare is an invaluable resource for DNB Radiology aspirants navigating the OSCE format. The structured guidance on preparation strategies, such as focusing on key systems, practicing with time constraints, and reviewing common pitfalls, is particularly beneficial. The emphasis on practical tips—like ensuring clear visibility of the screen during the exam and being prepared with extra stationery—demonstrates a thoughtful approach to real-world challenges candidates may face. Additionally, the inclusion of sample questions and a downloadable PDF of common OSCE question types provides readers with tangible tools to enhance their preparation. Overall, this comprehensive guide not only demystifies the OSCE process but also equips candidates with actionable insights to approach the exam with confidence.
RadioGyan