Key Takeaway:
To become an interventional radiologist in the United States, you can choose from two main pathways: the Integrated IR residency, a five-year program for medical students, or the Independent IR residency, a two-year program for graduates of a diagnostic radiology residency. Some diagnostic radiology residencies also offer an Early Specialization in Interventional Radiology (ESIR) designation, allowing residents to complete an independent IR residency in just one year.
Introduction
Welcome to the journey of becoming an interventional radiologist. As a medical professional, you have chosen a path that combines cutting-edge technology, clinical expertise, and a passion for helping patients. In this blog, we will delve into the steps you need to take from medical school to residency to ultimately become an interventional radiologist. This exciting field offers a rewarding career with numerous opportunities for growth and advancement. Join us as we explore the path to becoming an interventional radiologist and the integral role this specialty plays in the medical field.
Overview of the path to becoming an interventional radiologist
To become an interventional radiologist, you must complete several years of education and training. After completing a four-year undergraduate program, you’ll need to attend medical school for another four years. Once you’ve earned your medical degree, you’ll then need to complete a four-year residency program in diagnostic radiology. After finishing residency, you’ll have the option to pursue a two-year fellowship in interventional radiology. Throughout this journey, you’ll need to pass various standardized exams, such as the SAT, MCAT, and USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK.

Importance of interventional radiology in medical field
Interventional radiology plays a crucial role in the evolving landscape of modern medicine. As an interventional radiologist, you have the unique ability to diagnose and treat diseases using minimally invasive techniques. This approach minimizes risks, reduces recovery time, and improves patient outcomes. Interventional radiology techniques are employed in a wide range of medical conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer treatment, and management of various organ systems. From angioplasty to image-guided biopsies, interventional radiology offers innovative solutions that continue to revolutionize patient care. By choosing this field, you become an integral part of advancing medical science and improving quality of life for patients.
Pre-Medical Education
To embark on the path of becoming an interventional radiologist, you need to start by completing an undergraduate program. During your four years of pre-medical education, it is important to take prerequisite courses in biology, chemistry, physics, and math. Maintain a high GPA to enhance your chances of getting into medical school. Engaging in extracurricular activities, such as volunteer work and research, can also strengthen your application. Admissions committees look for well-rounded individuals who demonstrate a commitment to serving others and a passion for medicine.
Requisite undergraduate courses and degree
To become an interventional radiologist, you need to complete an undergraduate program that includes prerequisite courses in biology, chemistry, physics, and math. These courses provide you with a strong foundation in the sciences, which is essential for medical school. Additionally, it is important to earn a bachelor’s degree in a related field, such as biology or pre-medicine. This degree demonstrates your academic commitment and prepares you for the rigorous coursework ahead in medical school and residency training.
Importance of maintaining high GPA and extracurricular activities
Maintaining a high GPA is crucial for aspiring interventional radiologists. Admissions committees often consider academic performance as an indicator of dedication and ability to handle the rigorous coursework in medical school and residency. A strong GPA demonstrates your commitment to academic excellence. In addition to academics, participating in extracurricular activities such as research, volunteer work, and leadership roles enhances your application, showcasing a well-rounded profile and your ability to effectively manage time and responsibilities. Strive for excellence both inside and outside the classroom to increase your chances of success in your journey to becoming an interventional radiologist.
Medical School
During medical school, you will further develop your medical knowledge and clinical skills. The admission process includes fulfilling prerequisites, such as completing the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) and submitting applications to medical schools. Once accepted, you will embark on a rigorous curriculum that covers basic sciences, clinical rotations, and electives. These rotations provide hands-on experience in various specialties, including radiology. It is during this time that you can explore your interest in interventional radiology through elective rotations or research opportunities. Medical school prepares you for the next step in your journey towards becoming an interventional radiologist.
Admission process and requirements
To pursue a career as an interventional radiologist, you must first gain admission to medical school. The admission process typically involves completing the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) and submitting applications to medical schools. Additionally, you will need to demonstrate a strong academic record, including a high GPA, and participate in relevant extracurricular activities. Admissions committees also consider letters of recommendation, personal statements, and interviews. It is important to thoroughly research and comply with each school’s specific admission requirements to increase your chances of acceptance.
Rigorous curriculum and clinical rotations
During your time in medical school, you will experience a rigorous curriculum specifically designed to prepare you for a career in interventional radiology. The curriculum will cover a wide range of topics, including anatomy, physiology, medical imaging, and radiology techniques. Additionally, you will have the opportunity to participate in clinical rotations, where you will work directly with patients under the guidance of experienced physicians. These rotations will allow you to gain hands-on experience in performing various interventional radiology procedures and hone your skills in patient care and decision-making. You will also have the chance to learn from interdisciplinary teams and collaborate with other healthcare professionals. Overall, the combination of a challenging curriculum and clinical rotations will provide you with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in the field of interventional radiology.
Choosing a Specialty
When it comes to choosing a specialty in medicine, there are many factors to consider. As you embark on your journey towards becoming an interventional radiologist, it is important to carefully evaluate your interests, skills, and goals. Consider the unique advantages of interventional radiology, such as the ability to provide minimally invasive treatments and make a meaningful impact on patient outcomes. Additionally, be aware of the challenges that come with this specialty, such as the need for technical proficiency and the fast-paced nature of the field. Ultimately, choose a specialty that aligns with your passions and offers opportunities for growth and fulfillment in your career as an interventional radiologist.
Considerations for selecting interventional radiology as a specialty
When choosing a specialty in medicine, there are several factors to consider before deciding to pursue interventional radiology. First, evaluate your interest in the field’s unique advantages, such as the ability to provide minimally invasive treatments and make a significant impact on patient outcomes. Second, assess your technical skills and proficiency, as interventional radiologists require precise techniques and knowledge of imaging modalities. Finally, be prepared for the fast-paced nature of interventional radiology, as it often involves urgent and emergent cases. Taking these considerations into account will help you determine if interventional radiology is the right specialty for you.
Check out our detailed guide regarding Interventional Radiology :
Benefits and challenges of interventional radiology
Interventional radiology offers several benefits as a medical specialty. As an interventional radiologist, you have the opportunity to provide minimally invasive treatments, which often result in faster recovery times and fewer complications for patients. Additionally, you can make a significant impact on patient outcomes by using imaging-guided procedures to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions. However, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges of interventional radiology. The field requires a high level of technical skill and proficiency in imaging modalities. It also involves a fast-paced environment with urgent and emergent cases. Balancing these benefits and challenges is essential for a successful career in interventional radiology.
Residency Training
Residency training is a crucial step in becoming an interventional radiologist. During residency, you will gain hands-on experience and develop the necessary skills to provide high-quality patient care. The application process for interventional radiology residency programs typically involves submitting your academic records, letters of recommendation, and personal statement. If accepted, you will undergo several years of rigorous training, including rotations in various subspecialties within radiology. The duration of residency training in interventional radiology is typically four years. Throughout this period, you will have the opportunity to refine your technical skills and knowledge under the guidance of experienced faculty members. Completion of residency is followed by the option to pursue fellowship training in interventional radiology to gain further specialization.
These paths to become an interventional radiologists depend on which country you intend to practice. This is a general overview.
Application and selection process for interventional radiology residency
When applying for interventional radiology residency programs, you will need to submit your academic records, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement that highlights your interest in and commitment to the field. It is important to showcase your academic achievements, clinical experience, and research involvement. The selection process typically involves interviews, during which you will have the opportunity to demonstrate your knowledge, skills, and passion for interventional radiology. It is essential to be well-prepared and showcase your dedication to the field during the interview process.
Duration and requirements of residency training
During your residency training in interventional radiology, you will spend several years acquiring the necessary skills and knowledge to become a competent interventional radiologist. The duration of residency typically lasts four years, during which you will rotate through various clinical settings, honing your diagnostic and interventional skills. Additionally, you will be required to meet specific educational milestones and complete research projects to demonstrate your proficiency in the field. Successful completion of residency is a prerequisite for obtaining board certification and becoming a practicing interventional radiologist.
How do I become an interventional radiologist in the United States?
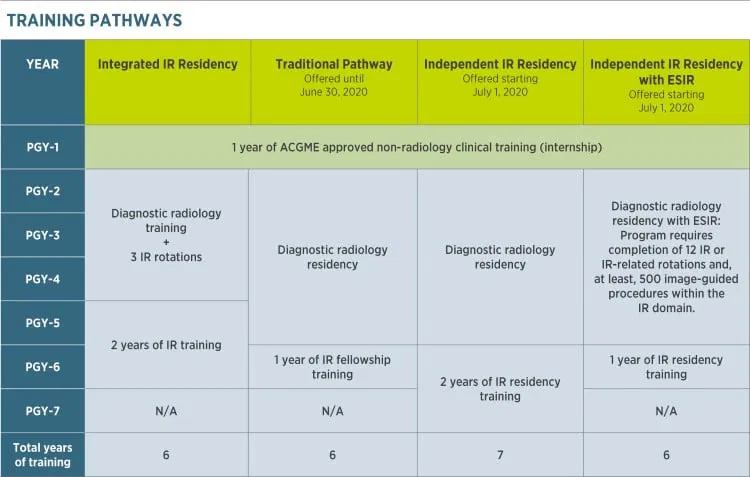
Integrated IR Residency
- Duration: Five years (including one internship year).
- Curriculum: Emphasis on diagnostic radiology for the first three years, followed by two years focused on interventional radiology.
- Eligibility: Open to medical students.
Independent IR Residency
- Duration: Two years.
- Eligibility: Exclusive to graduates of a diagnostic radiology residency.
Early Specialization in Interventional Radiology (ESIR)
- Graduates of diagnostic radiology residencies with ESIR designation may complete the independent IR residency in one year.
IR/DR Certification
- Graduates qualify for the IR/DR examination, recognizing competency in both diagnostic and interventional radiology.
Further reading: Society of Interventional Radiology and American Board of Radiology
How do I become an interventional radiologist in Canada?
Currently, the training pathway involves completing a 5-year Diagnostic Radiology Residency followed by a 1-year IR Fellowship.
In the near future, there will be changes to the training pathway. Specifically, the duration of IR training will be extended to 2 years. However, 1 year of this extended training will be double-counted within the diagnostic radiology training. This modification aims to provide more extensive training in clinical skills and IR related imaging. Importantly, despite these changes, the total length of the training program will remain the same at 6 years.
Future possibilities for IR training: In the more distant future, there is a potential for IR to become its own specialty with its own dedicated residency program. This would further enhance the focus and expertise in the field of IR.
Further reading: Canadian Association for Interventional Radiology
How do I become an interventional radiologist in the United Kingdom (UK)?
To become an interventional radiologist in the UK, join a clinical radiology training program that offers sub-specialty training in interventional radiology. Choose a scheme with comprehensive IR procedures. Transfer may be possible if IR training is not available. Decide on your sub-specialty, including IR, around the midpoint of your third year. Competition for IR training is rare. Schemes strive to provide nearby training if they can’t offer it themselves.
Further reading: British Society of Interventional Radiology (BSIR)
How do I become an interventional radiologist in Australia?
The journey to become an interventional radiologist starts with the RANZCR Clinical Radiology Training Program. In this program, registrars develop the basic procedural and clinical skills needed for interventional practice. This training program provides a foundation that can be further enhanced through Continuing Professional Development (CPD) activities or by pursuing a Fellowship in Interventional Radiology (IR) or Interventional Neuroradiology (INR) after receiving the FRANZCR qualification.
Completing a Fellowship in IR or INR allows radiologists to perform complex procedures that require specialized interventional skills. As hospitals recognize the value of IR and INR in improving patient outcomes and cost-efficiency, many radiologists who complete these Fellowships go on to work as full-time IR or INR consultants.
A Fellowship in Interventional Radiology usually lasts for one year. After completing the Fellowship, some IRs may choose to take the European Board of Interventional Radiology (EBIR) examination offered by CIRSE.
On the other hand, a Fellowship in Interventional Neuroradiology typically lasts for a minimum of two years. After completing this Fellowship, INRs can apply for recognition of their training in INR through the Conjoint Committee for the Recognition of Training in Interventional Neuroradiology (CCINR).
Fellowship opportunities are available at major hospitals and some regional centers. To find current Fellowship opportunities, you can visit the RANZCR Jobs website.
Further reading: RANZCR
Comparison of Interventional Radiology Pathway:
Dr. Mandal et al summarized the IR pathway in 5 english speaking countries in their 2020 BJR article:
| Country | UK | USA | CANADA | AUSTRALIA & NEW ZEALAND |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualification name | CCT in Clinical Radiology with Subspecialisation in IR | ABR Board Certification in DR & IR | Royal College Certification in DR & Royal College Certification in IR | FRANZCR & IRSA/CCINR Credentials |
| PG Years | FY1 | Internship | PGY1 Basic Clinical Year | Internship |
| FY2 | PGY2 DR | PGY2 DR | Internship (NZ) Residency (Aus) | |
| ST1 in DR | PGY3 DR | PGY3 DR | Year 1 Radiology | |
| ST2 in DR | PGY4 in DR | PGY4 DR | Year 2 Radiology | |
| ST3 in DR | PGY5 in IR | PGY5 DR | Year 3 Radiology | |
| ST4 in IR | PGY6 in IR | PGY6 IR Fellowship | Year 4 Radiology | |
| ST5 in IR | PGY7 IR Fellowship (dependent on previous exp.) | Year 5 Radiology | ||
| ST6 in IR | IR or INR Fellowship | |||
| INR Fellowship | ||||
| Min. PG Years of training | 8 | 6 | 6–7 | 8–9 |
| Years of radiology (IR) | 6 (3) | 5 (2) | 6-7(2) | 6-7 (1–2) Aus |
ABR, American Board of Radiology; CCINR, Conjoint Committee for Recognition of Training in Interventional Neuroradiology;CCT, Certificate of Completion of Training; DR, Diagnostic Radiology; FRANZCR, Fellowship of the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologist; INR, Interventional Neuroradiology; IR, Interventional Radiology; IRSA, Interventional Radiology Society of Australasia; PG, Postgraduate.
Career Opportunities and Future Outlook
As an aspiring interventional radiologist, you can look forward to promising career opportunities and a bright future in the field. Interventional radiology is a rapidly growing specialty with a high demand for skilled professionals. You can find employment in hospitals, outpatient clinics, and private practices. The field offers a wide range of procedures and the opportunity to work with cutting-edge technology. Additionally, interventional radiology offers a competitive salary and potential for career advancement. With advancements in medical imaging and minimally invasive procedures, the future of interventional radiology looks promising and exciting.
Job prospects and growth in the field of interventional radiology:
The field of interventional radiology presents promising job prospects and significant growth opportunities. As medical advancements continue to evolve, the demand for skilled interventional radiologists is on the rise. With an aging population and increased prevalence of chronic diseases, interventional radiology procedures are becoming more crucial in diagnosing and treating patients. As a result, there is a growing need for professionals in this specialized field, leading to a positive outlook for job opportunities. Furthermore, the field of interventional radiology offers a wide range of career paths and subspecialties, allowing professionals to focus on areas of interest and expertise.
How Much Do Interventional Radiologists Make an Hour?
Interventional radiologists earn a competitive salary for their specialized skills and expertise. On average, interventional radiologists make an excellent hourly wage. However, the exact salary can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, and the specific healthcare setting. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median hourly wage for radiologists, including those in interventional radiology, was $102.64 in May 2020.
It is important to note that interventional radiologists often enjoy additional benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, which contribute to their overall compensation package.
Continuing education and subspecialties in interventional radiology:
Continuing education is vital for interventional radiologists to stay updated with the latest techniques, equipment, and advancements in the field. Medical technology and procedures constantly evolve, making it crucial for professionals to engage in ongoing learning. Interventional radiologists have the opportunity to pursue subspecialties within their field, allowing them to develop expertise in specific areas. Subspecialties can include interventional oncology, vascular interventions, neurointerventions, pediatric interventions, and more. These subspecialties not only enhance job prospects but also enable interventional radiologists to make significant contributions to patient care in specialized areas. Continued education and subspecialties ensure that interventional radiologists remain at the forefront of advancements, allowing them to provide the highest level of medical care to their patients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey to becoming an interventional radiologist requires dedication, academic excellence, and a passion for patient care. From completing pre-medical education and medical school to undergoing rigorous residency training, aspiring interventional radiologists acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to provide minimally invasive treatments and make a significant impact on patient outcomes. The field of interventional radiology offers promising career opportunities, a competitive salary, and the potential for growth and advancement. With the continuous advancements in medical imaging and procedures, the future of interventional radiology looks bright and exciting. By choosing this specialty, individuals can contribute to the evolving landscape of modern medicine and improve the quality of life for their patients.