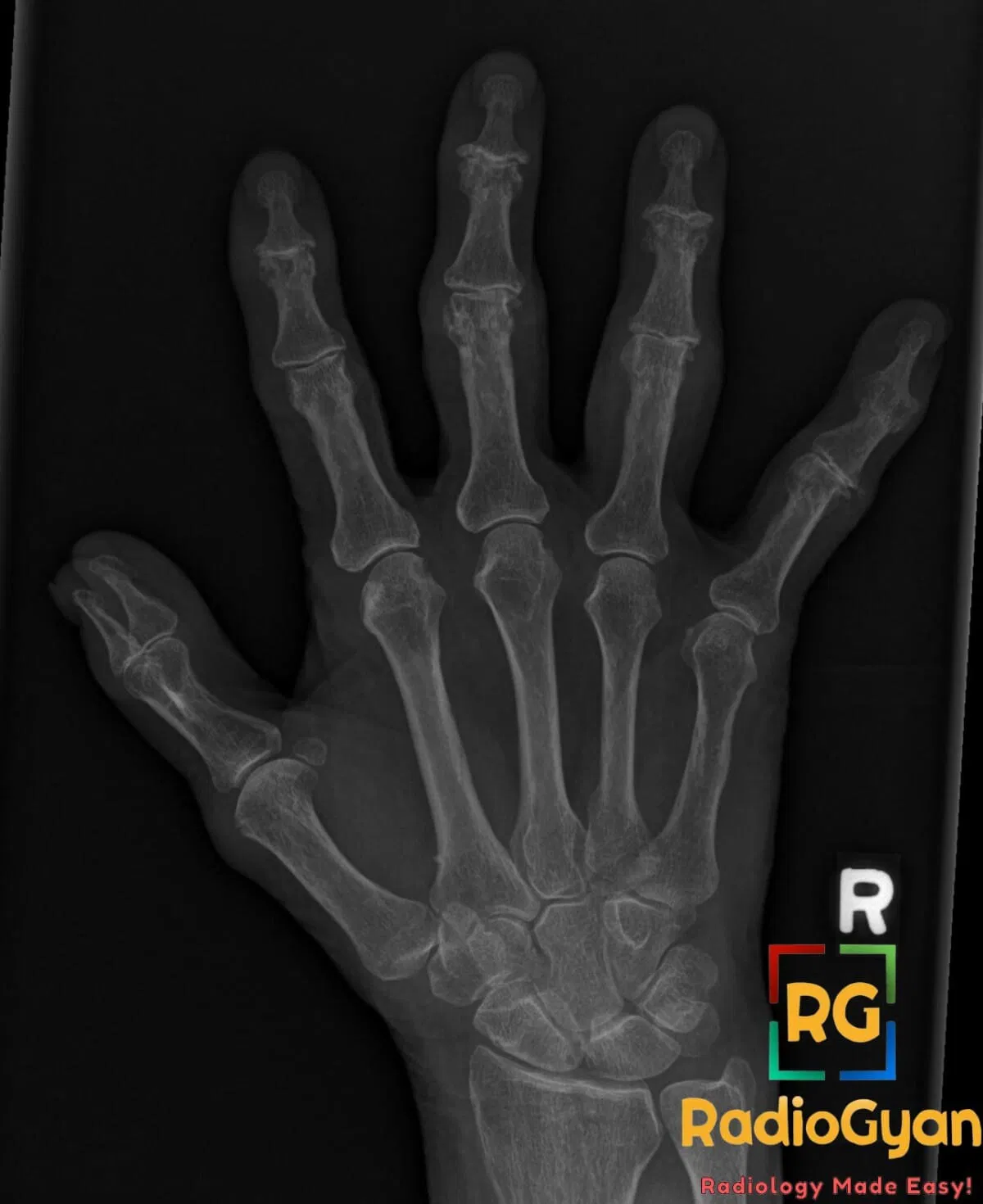
What causes gullwing appearance in the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints on plain radiographs?
Let me know in the comments.
Click to reveal the answer
Answer:
The gullwing appearance is caused by erosive changes in the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints characterized by central erosions with surrounding subchondral sclerosis and marginal osteophyte formation. This is a hallmark radiographic feature of erosive osteoarthritis, an inflammatory subtype of osteoarthritis affecting the DIP joints, producing pain, stiffness, and joint deformity.
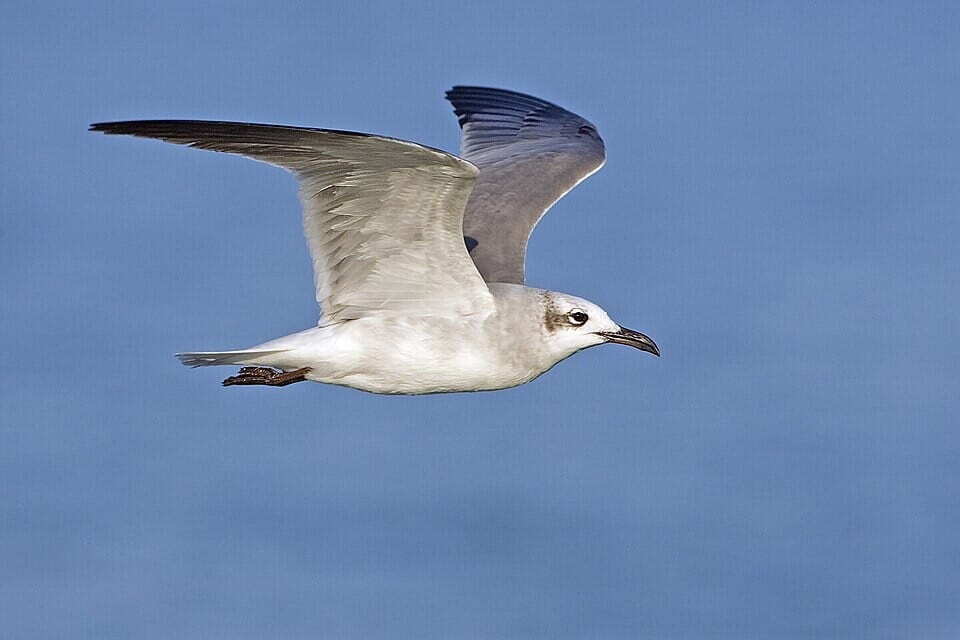
Why is it called so?
The term “gullwing” derives from the radiographic outline of the joint erosions and osteophytes resembling the wings of a seagull in flight—two symmetrical concave erosions centrally with sclerotic margins on either side, creating a bilobed shape similar to a gull’s wings.

Pathophysiology
The gullwing appearance develops due to an initial central subchondral bone erosion in the DIP joint caused by inflammation and cartilage loss. This central erosion is flanked by new bone formation at the joint margins (osteophytes) and reactive subchondral sclerosis. The combination of central erosions and peripheral bone proliferation leads to the characteristic bilobed radiographic contour.
Alternative names: Seagull erosions, sawtooth appearance
Other associated named signs: None specifically linked to erosive osteoarthritis but other osteoarthritic changes such as joint space narrowing and subchondral cysts may be present.
Access all radiology signs posted so far: https://radiogyan.com/radiology-signs/