TL;DR
Imaging features of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) on CT
Following features are NOT seen, typically in the early stages:
Please remember this important caveat though:
- Imaging features of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) on CT
- Typical Imaging features of for pulmonary involvement of COVID-19
- Sample cases: CT findings in patients with proven COVID-19 pneumonia
- Video lectures for CT imaging features of COVID-19 pneumonia
- FREE case collections for imaging of coronavirus pneumonia (includes DICOM datasets for AI)
- Temporal distribution of CT findings in patients with COVID pneumonia:
- Role of radiology in the diagnosis of COVID-19 / Novel COVID-19–infected pneumonia (NCIP)
- Reporting templates for COVID-19 pneumonia
- The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Fleischner Society Consensus
- Recommended Protocol for CT chest in coronavirus pneumonia
- Precautions for Radiology Department Personnel
- Resources and further reading
Typical Imaging features of for pulmonary involvement of COVID-19
Obligatory features:
- Ground-glass opacities, with or without consolidations, in lung regions close to visceral pleural surfaces, including the fissures (subpleural sparing is allowed) AND
- Multifocal bilateral distribution
Confirmatory patterns:
- Ground-glass regions
- Unsharp demarcation, (half) rounded shape.
- Sharp demarcation, outlining the shape of multiple adjacent secondary.
- Pulmonary lobules.
- Crazy paving.
- Patterns compatible with organizing pneumonia.
- Thickened vessels within parenchymal abnormalities found in all confirmatory patterns.
Reference: CO-RADS – A categorical CT assessment scheme for patients with suspected COVID-19: definition and evaluation.
Sample cases: CT findings in patients with proven COVID-19 pneumonia
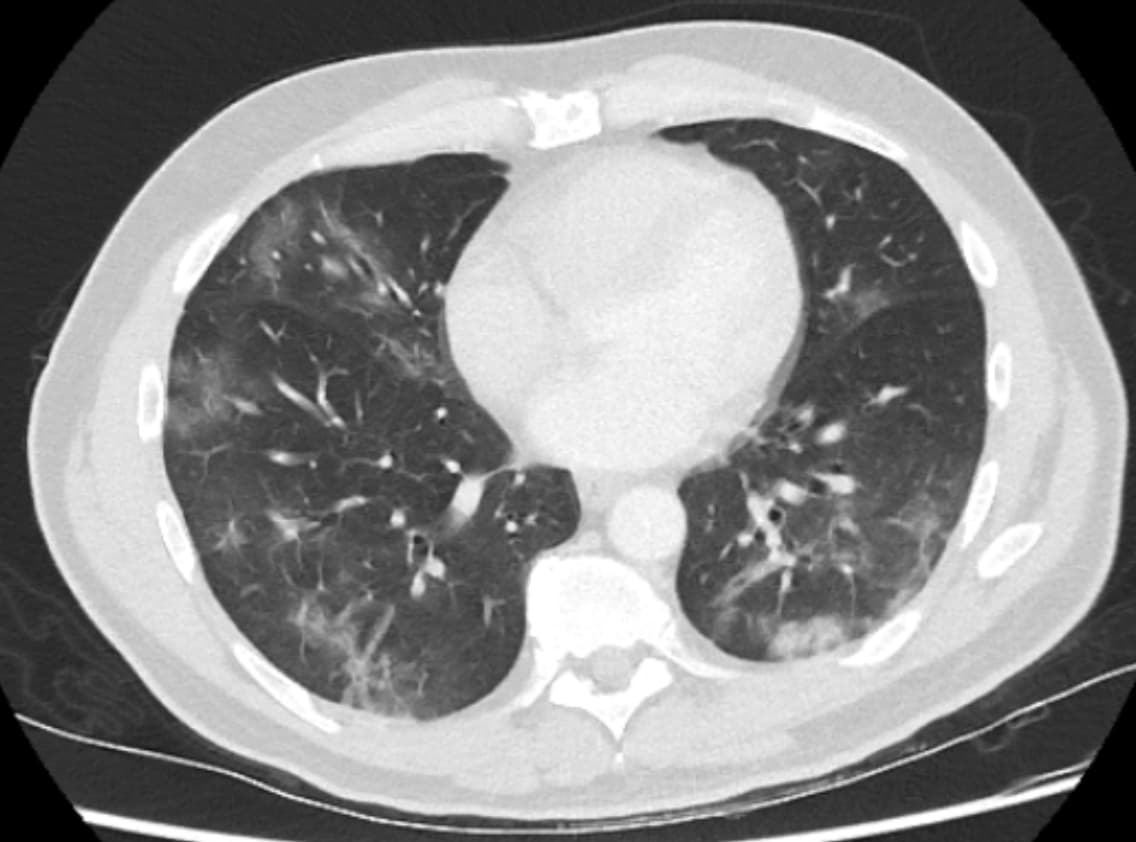
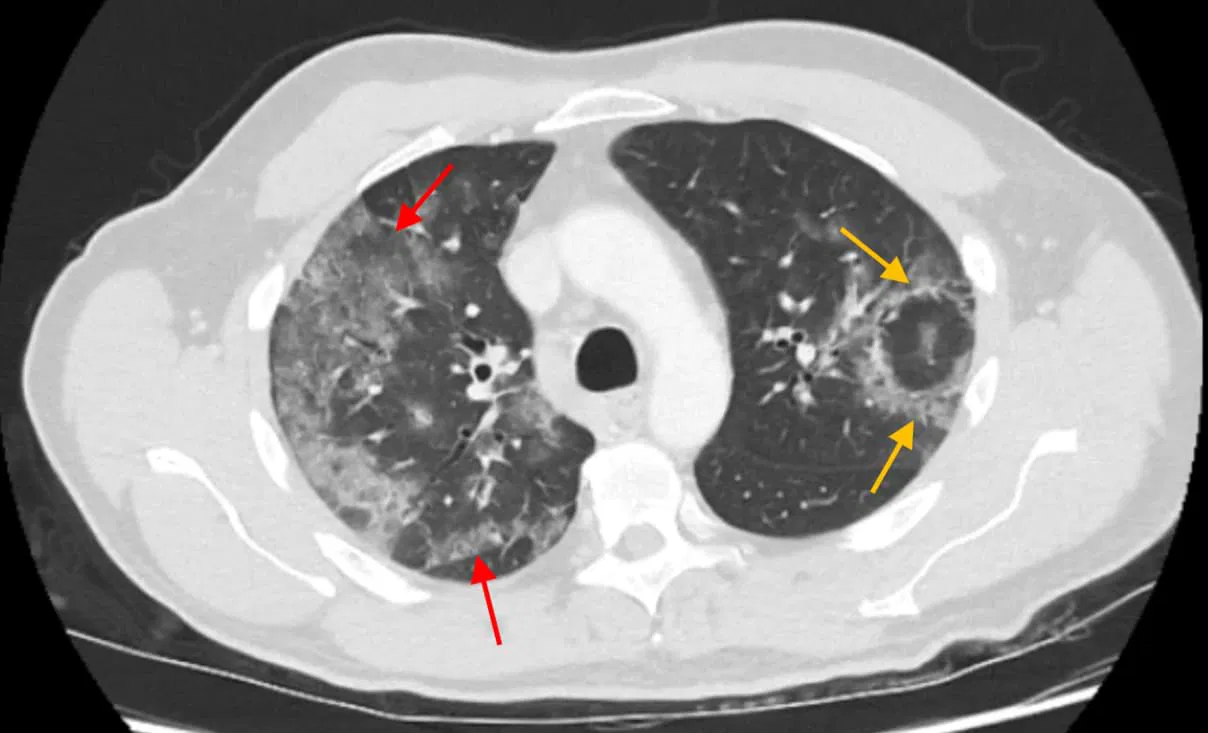
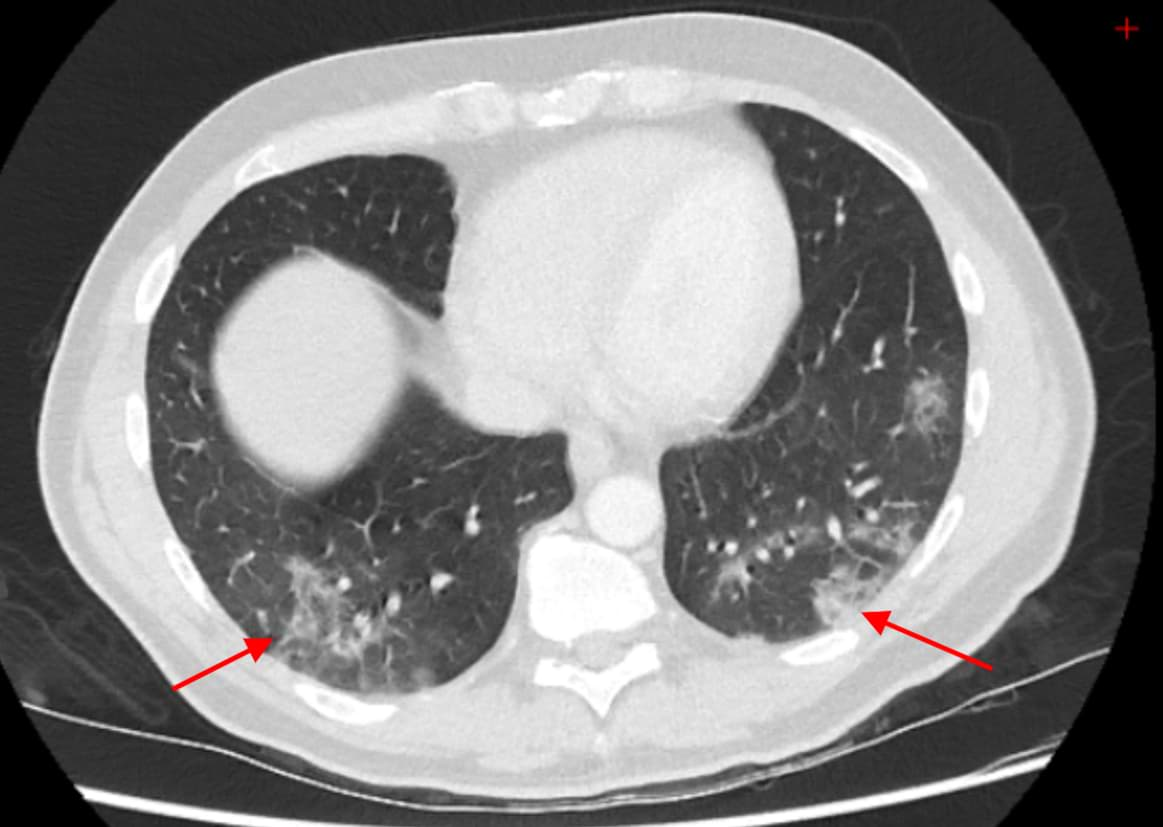
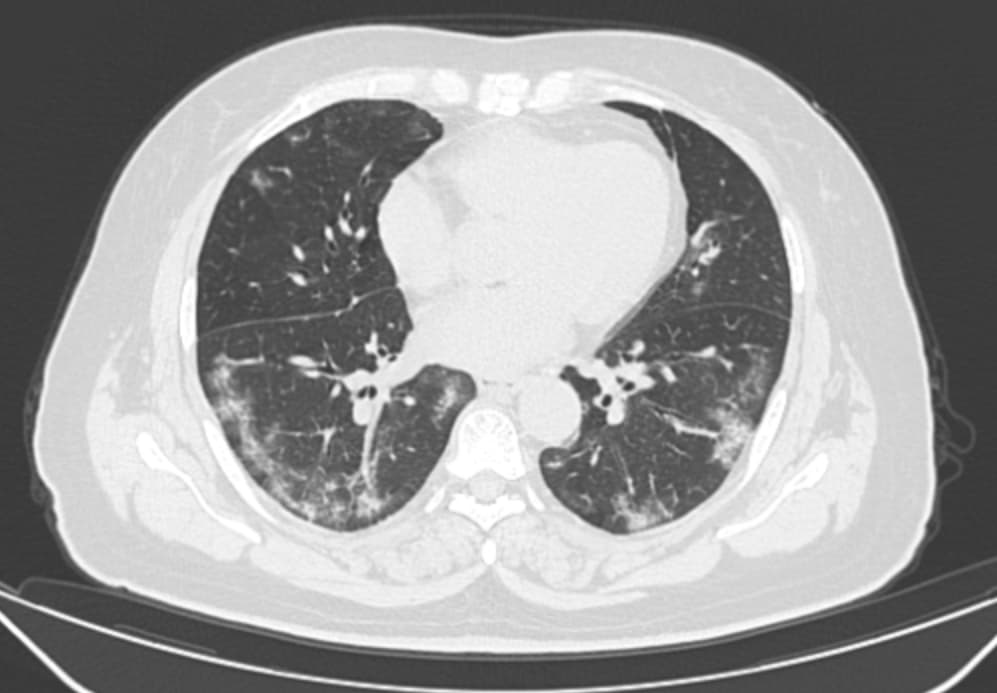
More radiology cases and resources available on our telegram channel: RadioGyan Telegram channel.
Video lectures for CT imaging features of COVID-19 pneumonia
Comprehensive 3- video playlist by RSNA covering the important imaging features of coronavirus and the role of radiology. Inlcudes:
1. A review of CXR and CT Findings of COVID-19.
2. The systems for structured reporting of those findings.
3. A description of how the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center has implemented structured reporting into their system.
Dr. Joseph Owen covers major imaging features of coronavirus pneumonia in this video:
uOttawa CME hosted by Dr. Carole Dennie, President of the Canadian Thoracic Society of Radiology on COVID-19 CT chest recognition:
Radiology fighting COVID-19 – Live report from Parma, Italy – Prof. Nicola Sverzellati
Imaging Findings of CoVID-19: More Than Just Ground Glass Opacities, by Henry Guo, MD, PhD
Illustrated video by Osmosis on imaging features of SARS-CoV 2 pneumonia
FREE case collections for imaging of coronavirus pneumonia (includes DICOM datasets for AI)
- Lecture on imaging features coronavirus by the Society of Thoracic Radiology. (RECOMMENDED) – The discussion on imaging features starts at 30:00.
- Italian Radiological Society COVID-19 database – More than 50 cases (still images).
- British Society of Thoracic Radiology COVID-19 database – DICOM sets of CXR and CT.
- COVID case collection by Dr. Daniel Ortiz on Twitter.
- RAIOSS & Livon Saúde : DICOM sets of cases (10 CT cases as of today)
- Cases from College of Radiologists, Singapore.
- RSNA coronavirus case collection.
FREE DICOM COVID-19 radiology images for Artificial Intelligence studies
- COVID-positive CT Scans
- COVID-positive x-rays
- COVID-negative x-rays
- Zhang Lab – these include normal and pneumonia x-rays.
- NIH Sample
- Unknown
- covid-19-pos-case – nothing is known about this data.
- Datasets
- Radiographs: Darshan Deshpande’s dataset
- CT: MedSeg’s dataset – sourced from SIRM.
Temporal distribution of CT findings in patients with COVID pneumonia:
| Timeline | Duration | Predominant finding |
|---|---|---|
| Early | 0-2 days | Normal CT chest |
| Intermediate | 3-5 days | Ground-glass opacities Consolidations Peripheral distribution of disease |
| Linear opacities | >6 days | Linear opacities |
Reference: Imaging features coronavirus
Role of radiology in the diagnosis of COVID-19 / Novel COVID-19–infected pneumonia (NCIP)
Here is what the radiology imaging societies are recommending worldwide:
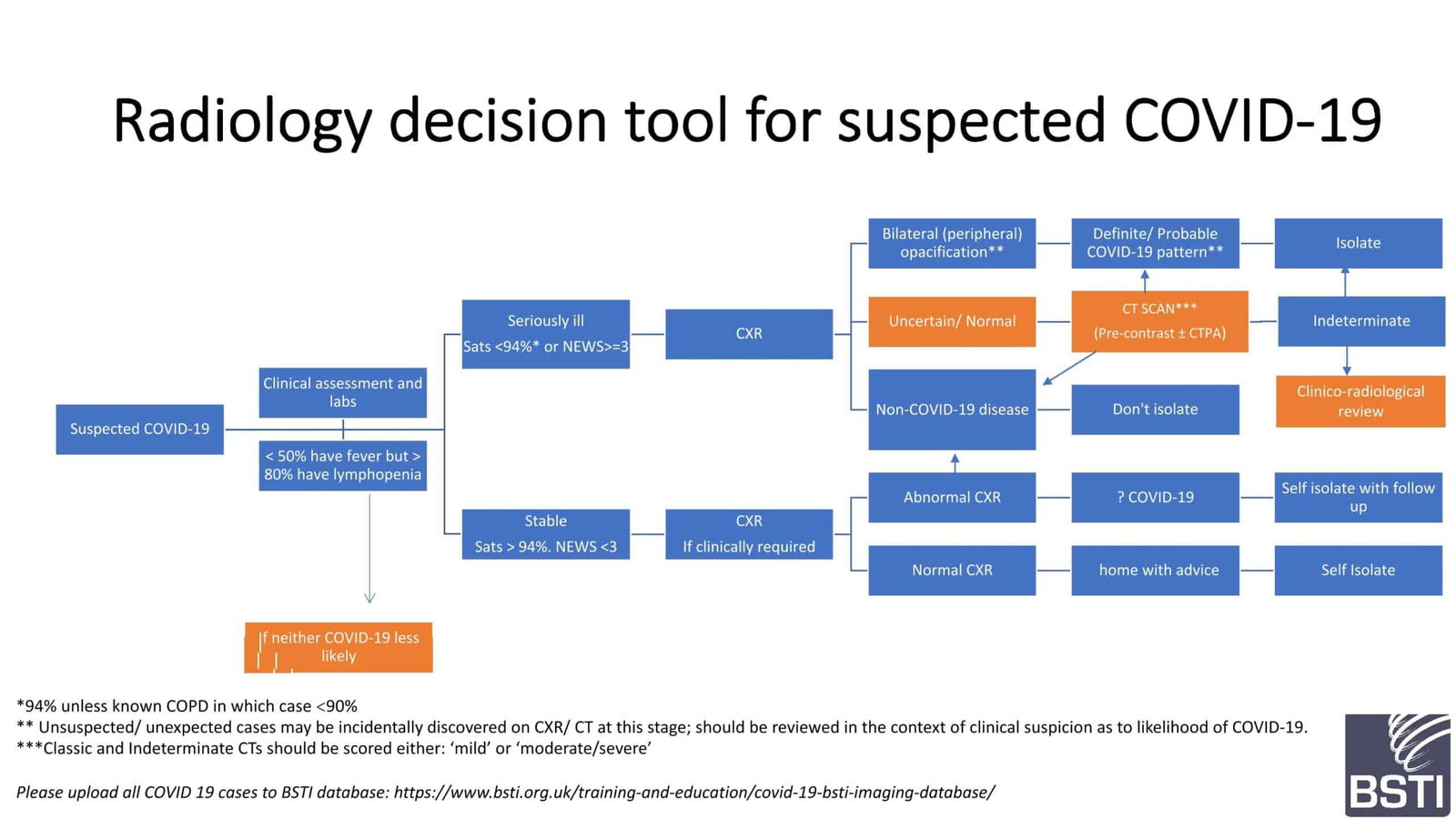
Reporting templates for COVID-19 pneumonia
The British Society of Thoracic Imaging has issued guidelines for classifying the likelihood of coronavirus pneumonia and provided templates for reporting.
Here is a link to the guidelines: BTSI COVID-19 guidelines
Templates for reporting cases:
Chest x-ray reporting template : PDF version || Word version
CT reporting template: PDF version || Word version
Structured reporting template for #COVID19 by RSNA endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology and American College of Radiology:
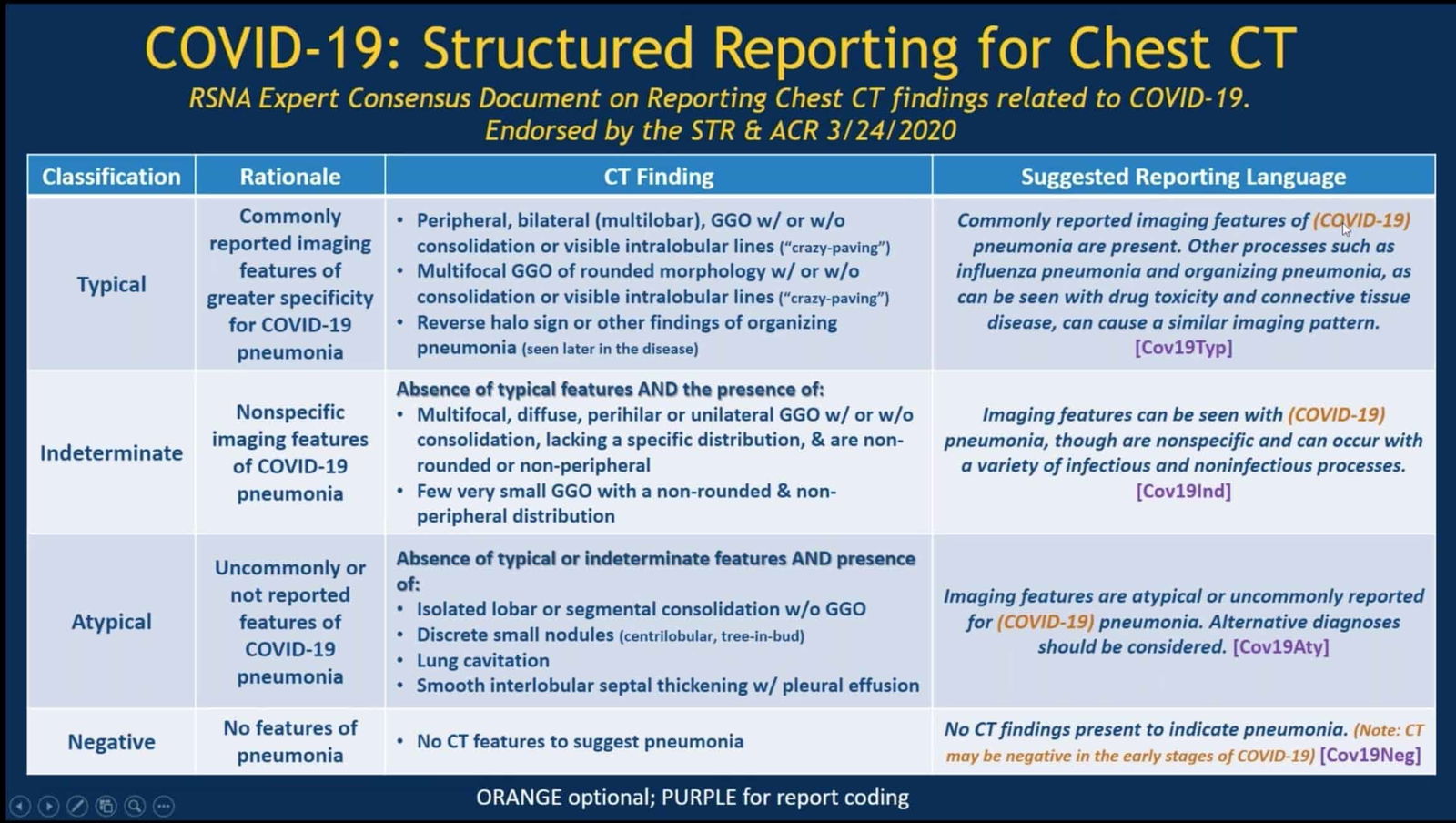
CO-RADS – COvid19 Reporting and Data System
The CO-RADS classification is a standardized reporting system for patients with suspected COVID-19 infection developed for a moderate to high prevalence setting. This was developed by the Dutch Radiological Society (NVvR) and published in Radiology.
Reference: CO-RADS – A categorical CT assessment scheme for patients with suspected COVID-19: definition and evaluation.
The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Fleischner Society Consensus
Summary of Recommendations for Imaging for COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia) by the Fleishner Society
Main Recommendations
Imaging Recommended

- For patients with moderate to severe features of COVID-19 regardless of COVID-19 test results.
- For patients with COVID-19 and evidence of worsening respiratory status.
- In a resource-constrained environment where access to CT is limited, CXR may be preferred for patients with COVID-19 unless features of respiratory worsening
Imaging NOT routinely recommended

- As a screening test in asymptomatic individuals.
- Patients with mild features of COVID-19 unless they are at risk for disease progression.
Additional Recommendations
- Daily chest radiographs are NOT indicated in stable intubated patients with COVID-19
- CT is indicated in patients with functional impairment and/or hypoxemia after recovery from COVID-19.
- COVID-19 testing is indicated in patients incidentally found to have findings suggestive of COVID-19 on a CT scan.
Recommended Protocol for CT chest in coronavirus pneumonia
Recommendations by the Iranian Society of Radiology.
- Single breath-hold scan without oral or IV contrast.
- Parameters:
- Kvp: 100-120
- mAs: 50-100
- Pitch: 0.8-1.5
- Thickness: 1-3 mm
Precautions for Radiology Department Personnel
Ensuring the safety of healthcare workers and other patients is essential.
The Journal of American College of Radiology and Radiology (RSNA)journals have outlined a few recommendations for the safety of radiology personnel while managing patients with coronavirus pneumonia.
These articles are available for free download:
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Outbreak: What the Department of Radiology Should Know
- Radiology Department Preparedness for COVID-19: Radiology Scientific Expert Panel

Here are a few of the recommendations:
- Portable radiographic equipment should be used to limit the transportation of patients.
- If a patient needs to be transported to the radiology department, he or she should wear a surgical mask during transport to and from the department.
- Radiology equipment should be disinfected after every contact with suspected patients.
- Implementation of standard operating procedures for radiological imaging and procedures for patients with known or suspected COVlD-19 exposure.
- Improving capability for remote interpretations (home, other sites) in the case of staff isolation or patient surge.
How to clean ultrasound machines during the coronavirus pandemic?
Check this video by American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM):
Mindray Ultrasound cleaning guide:
Here are recommendations from the "SFM India Oriented Guidelines for Ultrasound Establishments During the COVID19 Pandemic"
SARSCoV2, the causative agent of COVID-19 can be present on surfaces for several days. Surfaces that come into contact with the patient (cable and transducer), as well as surfaces that are touched by the clinician (keyboard, touchscreen, trackball, handlebars, etc.), should be disinfected after each examination. High-level disinfection (HLD) is not required when using ultrasound probes on intact skin. There is no evidence that HLD offers benefits for disinfection from SARS-CoV2.
The following steps should be followed:
1. Excess ultrasound gel on the transducer should be wiped off with a soft cloth after each examination. The gel can harbor a lot of germs and its presence prevents adequate disinfection.
2. Transducer surfaces and cords should be wiped with an equipment vendor-approved low-level disinfectant (LLD). Commonly approved agents include 70% Alcohol, Ammonia, 10% Bleach, Clorox, standard dilute Cidex, Protex wipes, SaniCloth, PI Spray, Oxivir wipes, Mikrobac, Microzide, Lonza, Klercide 70 and Descocept wipes.
3. Equipment desktop, edges, keyboard, transducer resting stands and especially the side in close proximity to the patient should be wiped with an LLD.
4. Commercial wipes should not be reused. These should be disposed of in appropriate bins. Cloths may be laundered with standard machine-washing.
5. Transducer and cord covers are too overpriced for general use. Makeshift covers like laparoscopy camera covers are difficult to source. These are not encouraged and LLD is adequate.
6. Ultrasound machines in COVID designated centers must be used with machine covers and covers for the transducer and cable. High-level disinfectants (HLD) is recommended in areas if ultrasound has been done where AGPs were performed.
Cleaning Recommendations from Radiology Equipment Manufacturers and ultrasound organizations:
- AIUM: Guidelines for Cleaning and Preparing External- and Internal-Use Ultrasound Transducers and Equipment Between Patients as well as Safe Handling and Use of Ultrasound Coupling Gel
- AIUM: Quick Guide on COVID-19 Protections - Ultrasound Transducers, Equipment, and Gel
- AIUM: Quick Guide on COVID-19 Protections - Patient and Ultrasound Provider Protection
- WFUMB: How to Perform a Safe Ultrasound Examination and Clean Equipment
- WFUMB: Handbook of COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment
- ISUOG: Safety Committee Position Statement: Safe Performance of Obstetric and Gynecological Scans and Equipment Cleaning
Canon Medical Systems
- Guidelines for cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization of transducers -PDF version of latest disinfection guidelines for all Canon transducers
- Cleaning Guidelines -Link to page with cleaning guidelines and other resources; will be updated with guidelines specific to COVID-19 soon
- Canon Medical COVID-19 website
GE Healthcare
- Transducer Care site – https://www.gehealthcare.com/products/ultrasound/ultrasound-transducers – provides approved cleaners, disinfectants, and gels for all the various probes
- GE system cleaning site: https://cleaning.gehealthcare.com/ – provides cleaning instructions and details for the systems overall
- GE Healthcare COVID-19 Resources website
- GE Healthcare COVID-19 Cleaning & Disinfection FAQs
Hitachi Healthcare
Philips
- Compatible disinfectants and cleaning solutions for your Ultrasound system and transducers
- Philips COVID-19 Website
Siemens Healthineers
- Cleaner and Disinfectant Online Tool – Allows customers to search by system/transducer and find approved cleaning agents
Watch this webinar by RSNA on managing radiology workflow :
Radiology Preparedness for COVID-19: Radiology Scientific Expert Review Panel
Suggestions for Radiologists and radiology reporting rooms:
Social distancing is also an important measure while at the workplace. Here is a great twitter thread that discusses ways in radiologist can practice social distancing.
Posters for social distancing in Radiology departments during COVID-19 outbreak. Paste this on your reporting room door to minimize in person contact.

Some more resources for managing radiology department during this period:
- Old Threat, New Enemy: Is Your Interventional Radiology Service Ready for the Coronavirus Disease 2019?
- Déjà Vu or Jamais Vu? How the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Experience Influenced a Singapore Radiology Department's Response to the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Epidemic
- Is Your Interventional Radiology Service Ready for SARS?: The Singapore Experience
- Hiding in the Bunker: Challenges for a radiation oncology department operating in the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome outbreak
Resources and further reading
- Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection.
- RSNA COVID-19 coverage
- CT Features of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia in 62 Patients in Wuhan, China.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of Chest CT in Diagnosis and Management
- COVID-19 pneumonia: what has CT taught us?
- Essentials for Radiologists on COVID-19: An Update—Radiology Scientific Expert Panel
- Chest CT Findings in 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Infections from Wuhan, China: Key Points for the Radiologist
My 2 cents: Avoid non-emergent travel. Built-up your immunity. Avoid spreading rumors on social media. Trust only authentic sources to avoid panic. Stay safe.
DISCLAIMER: The content in this blog post is compiled from publically available sources as of March 16, 2020. The information is for medical health professionals, only for reference and not a substitute for clinical judgment









thank you sir. good compilations and links.
Glad you liked it, Abhijeet!
Very nicely compiled n Informative Article sir….
Glad you liked it, Salim.
-A