Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis – Radiology Board Review
- Clinical: Middle-aged men (peak 30-50 years); strong association with inflammatory bowel disease (particularly ulcerative colitis); progressive fatigue, pruritus, jaundice; increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma and colorectal cancer; may be asymptomatic with only elevated alkaline phosphatase
- Etiology/Pathophys: Chronic immune-mediated cholangiopathy causing progressive inflammatory fibrosis of intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts; leads to biliary strictures, cholestasis, and eventual cirrhosis; gut-liver axis involvement with altered microbiome
- Radiograph: Generally normal in early stages; may show hepatomegaly or features of portal hypertension in advanced disease
- US: Dilated intrahepatic bile ducts with irregular walls; echogenic portal tract thickening; hepatomegaly; splenomegaly in advanced cases; may show gallbladder wall thickening
- CT: Alternating strictures and dilatations of bile ducts creating “beading” appearance; wall thickening of bile ducts; hepatomegaly; portal lymphadenopathy; signs of cirrhosis and portal hypertension in advanced disease
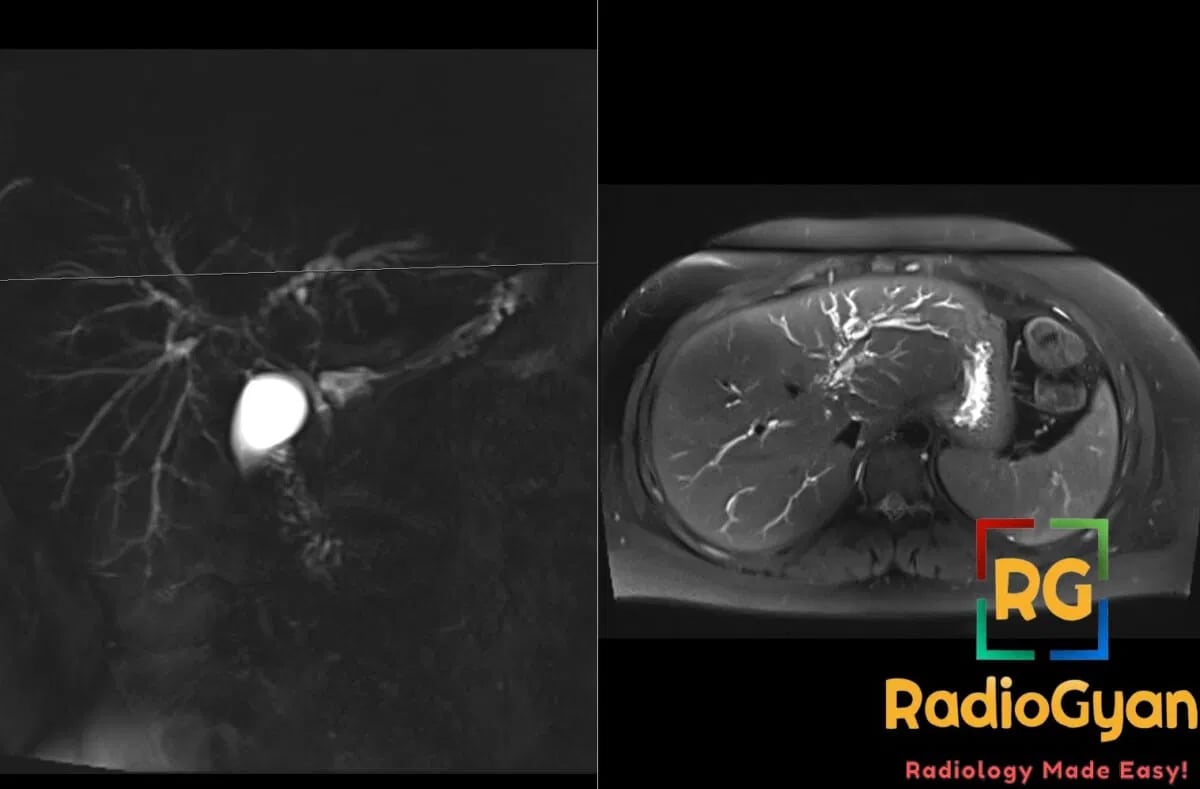
- MRI: MRCP is diagnostic modality of choice; classic “string of beads” sign with alternating strictures and dilatations; pruned tree appearance of intrahepatic ducts; T2 hyperintense periductal thickening; dominant strictures appear as severe focal narrowing
- Signs: String of beads sign – alternating strictures and dilatations on MRCP; pruned tree sign – loss of peripheral bile duct branching; periductal halo sign – T2 hyperintense rim around bile ducts
- Frameworks: Classification based on involvement: large duct PSC (classic), small duct PSC, PSC-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome; staging based on extent of ductal involvement and presence of cirrhosis
- DDx: Secondary sclerosing cholangitis (ischemic, infectious, toxic); cholangiocarcinoma (focal stricture, mass lesion); recurrent pyogenic cholangitis (stones, abscesses); IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (pancreatic involvement, elevated IgG4)
- Tx: UDCA for symptom management; endoscopic therapy for dominant strictures; liver transplantation for end-stage disease; radiologist monitors for cholangiocarcinoma development and disease progression